Page 375 - The History of the Royal Army Veterinary Corps 1962–2021
P. 375
to denote the forces assign
r.
he necessary control functions to enable the capability to be ap
structure, Personnel, Logis
,
maintained, prioritised, reconfigured and employed
r
c
ti
e
cs
In
THE HISTORY OF THE ROYAL ARMY VETERINARY CORPS 1962 – 2021
more recent operations in Northern Ireland, The Balkans, Iraq and Afghanistan41 has proved anew their particular utility. With their rapidly adaptable scent palate, MWD provide an agile and capable detection tool.42 They also give the ground commander the ability to deter, control or detain an individual or group without having to employ lethal force. As such, they have utility in offensive, defensive, stabilisation43 and enabling activities.
Under Army 2020 structures, the Field Army
will hold MWD and Veterinary capability at
appropriate readiness to provide scalable,
deployable MWD and Veterinary force elements
to support ground component operations at home
and abroad. These assets are vested in 1 MWD Regt,
which is configured primarily to provide combat
support to intervention operations, including
VHR contingency. The Regiment can also force
generate MWD and Veterinary capability in
support of Overseas Capacity Building44 and can
assist in military support to UK resilience activity.45
Command Control and Integration
Command, Control and Capability Management The Nature of MWD Capability centralised control and decentralised execution:
Field Army Organisation. Within the Field Army: The Role of MWD
source of deployable Army MWD capability.47
PROTECTION tactical functions. Using a spread of individual types of MWD, MWD capability operates predominantly in the Close Support (CS) role, but also provides General Support (GS) to
formation.
s
o
for
u
ma
m
r
e
t
m
ion
an
g
t
ed
47 The RAFP have some MWD capability, which can be used to reinforce support to Land Forces. SF MWD Capability is organic to UKSF.
48 The Defence Lines of Development are a Defence standard method of understanding the elements of capability: Training, Organisation, Equipment, Infra-
t
oa
c
o
de
d
,D
o
ctr
,
m
ine
an
a
n
d
Co
a
g
nc
ep
e
d
ts
.
49 ADP Operations, dated November 2010. Paragraph 0413 b. defines Combat Support, noting that this include “dog units”. Paragraph 0905.d.2, also states
that “Staff Support formerly included the provision of working dogs, dog handlers and veterinary services. These capabilities are also now regarded as
Veterinary
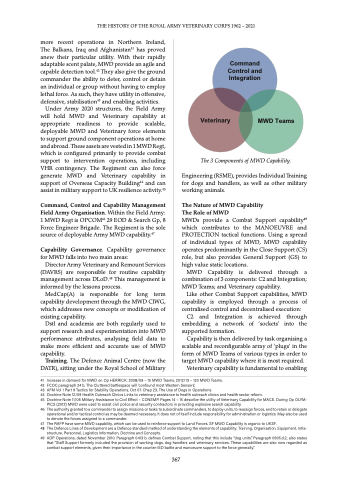
MWD Teams
The 3 Components of MWD Capability.
Figure 1 - 3 Components of MWD Capability.
Engineering (RSME), provides Individual Training
for dogs and handlers, as well as other military
working animals.
Like other Combat Support capabilities, MWD capability is employed thro
1 MWD Regt is OPCOM46 29 EOD & Search Gp, 8 MWDs provide a Combat Support capability49
Force Engineer Brigade. The Regiment is the sole which contributes to the MANOEUVRE and
C2 and Integration is achieved through embedding a network of ‘sockets’ i
Capability Governance. Capability governance for MWD falls into two main areas:
Director Army Veterinary and Remount Services high value static locations.
Capability is then delivered by task organising a scalable and reconfigurabl
(DAVRS) are responsible for routine capability MWD Capability is delivered through a
management across DLoD.48 This management is combination of 3 components: C2 and Integration;
in the form of MWD Teams of various types in order to target MWD capab
informed by the lessons process.
MedCap(A) is responsible for long term
MWD Teams; and Veterinary capability.
Like other Combat Support capabilities, MWD capability is employed through a process of
most required.
capability development through the MWD CIWG,
which addresses new concepts or modification of
existing capability. Veterinary capability is fundaCm2 eanntdal tInotegnraatibonlingis anacdhiseuvesdtaitnhirnouggMh WDs. It i
Dstl and academia are both regularly used to support research and experimentation into MWD
embedding a network of ‘sockets’ into the supported formation.
force element levels.
performance attributes, analysing field data to make more efficient and accurate use of MWD capability.
Training. The Defence Animal Centre (now the DATR), sitting under the Royal School of Military
Capability is then delivered by task organising a scalable and reconfigurable array of ‘plugs’ in the
centralised control and decentralised execution:
C2 and Integration
form of MWD Teams of various types in order to target MWD capability where it is most required.
Veterinary capability is fundamental to enabling
MWD capability needs to be commanded by the appropriate level of MW
41 Increase in demand for MWD on Op HERRICK: 2008/09 – 15 MWD Teams, 2012/13 – 120 MWD Teams.
42 FCOC paragraph 24 b. The Cluttered battlespace will ‘confound most Western Sensors.’
Charged with providing a single point of MWD advice to the formation, thi
43 AFM Vol 1 Part 9 Tactics for Stability Operations, Oct 07. Chap 23, The Use of Dogs in Operations.
44 Doctrine Note 12/09 Health Outreach Clinics Links to veterinary assistance to health outreach clinics and health sector reform.
45 Doctrine Note 11/06 Military Assistance to Civil Effect – CONEMP. Pages 14 – 15 describe the utility of Veterinary Capability for MACE. During Op OLYM-
must also be supported by a unit/sub-unit/detachment organisation whic
PICS (2012) MWD were used to assist civil police and security contractors in providing explosive search capability.
46 The authority granted to a commander to assign missions or tasks to subordinate commanders, to deploy units, to reassign forces, and to retain or delegate operational and/or tactical control as may be deemed necessary. It does not of itself include responsibility for administration or logistics. May also be used
p
o
d
r
v
i
i
n
This includes the need to: plan, resource and deliver continuation training;
combat support elements, given their importance in the counter-IED battle and manoeuvre support to the force generally.”
367
equipment support and veterinary support to the MWD force package; an reconfigure and redeploy assets across the operational area.
u n
e
s
D s
h p
a d