Page 173 - Physics Coursebook 2015 (A level)
P. 173
Chapter 11: Resistance and resistivity
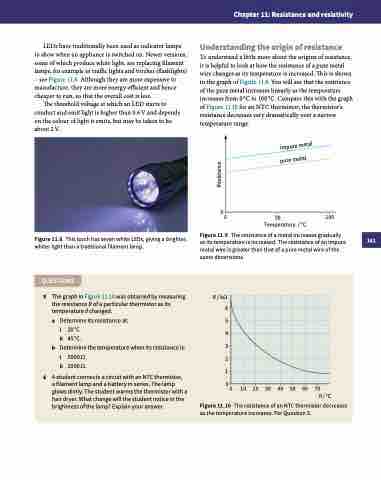
LEDs have traditionally been used as indicator lamps to show when an appliance is switched on. Newer versions, some of which produce white light, are replacing filament lamps, for example in traffic lights and torches (flashlights) – see Figure 11.8. Although they are more expensive to manufacture, they are more energy-efficient and hence cheaper to run, so that the overall cost is less.
The threshold voltage at which an LED starts to conduct and emit light is higher than 0.6 V and depends on the colour of light it emits, but may be taken to be about 2 V.
Figure 11.8 This torch has seven white LEDs, giving a brighter, whiter light than a traditional filament lamp.
QUESTIONS
5 The graph in Figure 11.10 was obtained by measuring the resistance R of a particular thermistor as its temperature θ changed.
a Determine its resistance at: i 20°C
ii 45 °C.
b Determine the temperature when its resistance is:
i 5000Ω ii 2000 Ω.
6 A student connects a circuit with an NTC thermistor,
a filament lamp and a battery in series. The lamp glows dimly. The student warms the thermistor with a hair dryer. What change will the student notice in the brightness of the lamp? Explain your answer.
Understanding the origin of resistance
To understand a little more about the origins of resistance, it is helpful to look at how the resistance of a pure metal wire changes as its temperature is increased. This is shown in the graph of Figure 11.9. You will see that the resistance of the pure metal increases linearly as the temperature increases from 0 °C to 100 °C. Compare this with the graph of Figure 11.10 for an NTC thermistor; the thermistor’s resistance decreases very dramatically over a narrow temperature range.
00 50 100 Temperature / °C
Figure 11.9 The resistance of a metal increases gradually as its temperature is increased. The resistance of an impure metal wire is greater than that of a pure metal wire of the same dimensions.
R / kΩ 6
5
4
3
2
1
0 0 10 20
30 40 50 60 70 θ/°C
Figure 11.10 The resistance of an NTC thermistor decreases as the temperature increases. For Question 5.
161
impure metal pure metal
Resistance