Page 320 - Physics Coursebook 2015 (A level)
P. 320
Cambridge International A Level Physics
10
9
When a cricket ball hits a cricket bat at high speed it can cause a standing wave to form on the bat. In one such example the handle of the bat moved with a frequency of 60 Hz with an amplitude of 2.8 mm.
The vibrational movement of the bat handle can be modelled on simple harmonic motion.
a State the conditions for simple harmonic motion. [2]
b Calculate the maximum acceleration of the bat handle. [2]
c Given that the part of the bat handle held by the cricketer has a mass of 0.48 kg, calculate the maximum
force produced on his hands. [1]
d The oscillations are damped and die away after about five complete cycles. Sketch a displacement–time
graph to show the oscillations. [2]
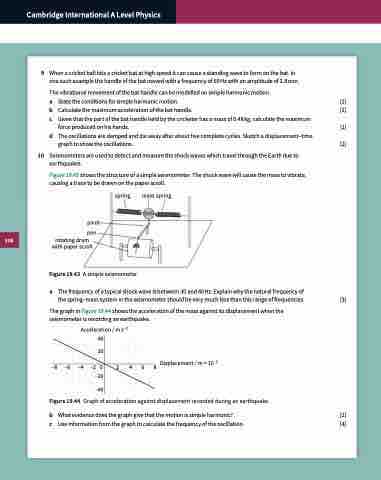
Seismometers are used to detect and measure the shock waves which travel through the Earth due to earthquakes.
Figure 19.43 shows the structure of a simple seismometer. The shock wave will cause the mass to vibrate, causing a trace to be drawn on the paper scroll.
spring
with paper scroll
Figure19.43 Asimpleseismometer.
mass spring
308
pivot
pen rotating drum
a The frequency of a typical shock wave is between 30 and 40 Hz. Explain why the natural frequency of
the spring–mass system in the seismometer should be very much less than this range of frequencies. [3]
The graph in Figure 19.44 shows the acceleration of the mass against its displacement when the seismometer is recording an earthquake.
Acceleration / m s–2 40
–8 8 Displacement / m × 10–2 –40
Figure 19.44 Graph of acceleration against displacement recorded during an earthquake.
b What evidence does the graph give that the motion is simple harmonic? [2]
c Use information from the graph to calculate the frequency of the oscillation. [4]
–6
–4
–2
20
–20
0
2
4
6