Page 365 - Understanding Psychology
P. 365
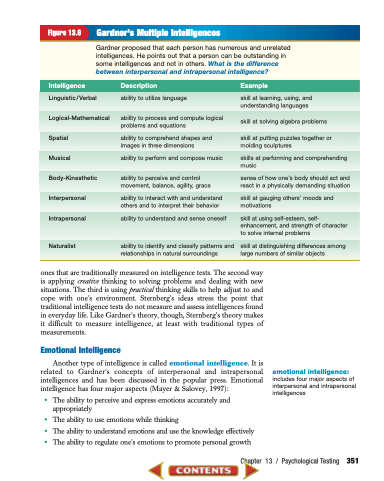
Figure 13.6 Gardner’s Multiple Intelligences
Gardner proposed that each person has numerous and unrelated intelligences. He points out that a person can be outstanding in some intelligences and not in others. What is the difference between interpersonal and intrapersonal intelligence?
Intelligence Description Example
Linguistic/Verbal Logical-Mathematical Spatial
Musical Body-Kinesthetic Interpersonal Intrapersonal
Naturalist
ability to utilize language
ability to process and compute logical problems and equations
ability to comprehend shapes and images in three dimensions
ability to perform and compose music
ability to perceive and control movement, balance, agility, grace
ability to interact with and understand others and to interpret their behavior
ability to understand and sense oneself
ability to identify and classify patterns and relationships in natural surroundings
skill at learning, using, and understanding languages
skill at solving algebra problems
skill at putting puzzles together or molding sculptures
skills at performing and comprehending music
sense of how one’s body should act and react in a physically demanding situation
skill at gauging others’ moods and motivations
skill at using self-esteem, self- enhancement, and strength of character to solve internal problems
skill at distinguishing differences among large numbers of similar objects
ones that are traditionally measured on intelligence tests. The second way is applying creative thinking to solving problems and dealing with new situations. The third is using practical thinking skills to help adjust to and cope with one’s environment. Sternberg’s ideas stress the point that traditional intelligence tests do not measure and assess intelligences found in everyday life. Like Gardner’s theory, though, Sternberg’s theory makes it difficult to measure intelligence, at least with traditional types of measurements.
Emotional Intelligence
Another type of intelligence is called emotional intelligence. It is related to Gardner’s concepts of interpersonal and intrapersonal intelligences and has been discussed in the popular press. Emotional intelligence has four major aspects (Mayer & Salovey, 1997):
• The ability to perceive and express emotions accurately and appropriately
• The ability to use emotions while thinking
• The ability to understand emotions and use the knowledge effectively
• The ability to regulate one’s emotions to promote personal growth
emotional intelligence:
includes four major aspects of interpersonal and intrapersonal intelligences
Chapter
13 /
Psychological Testing 351