Page 136 - Geosystems An Introduction to Physical Geography 4th Canadian Edition
P. 136
100
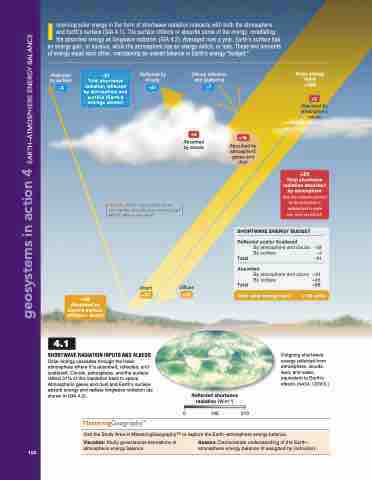
I ncoming solar energy in the form of shortwave radiation interacts with both the atmosphere and Earth’s surface (GIA 4.1). The surface reflects or absorbs some of the energy, reradiating the absorbed energy as longwave radiation (GIA 4.2). Averaged over a year, Earth’s surface has
an energy gain, or surplus, while the atmosphere has an energy deficit, or loss. These two amounts of energy equal each other, maintaining an overall balance in Earth’s energy “budget.”
Reflected by surface
–31
Total shortwave radiation reflected by atmosphere and surface (Earth's average albedo)
Reflected by clouds
–21
Diffuse reflection and scattering
–7
Solar energy input +100
+3
Absorbed by stratospheric ozone
+24
Total shortwave radiation absorbed by atmosphere Note that radiation absorbed by the atmosphere is radiated back to space over time (see GIA 4.2).
–3
+3
Absorbed by clouds
+18
Absorbed by atmospheric gases and dust
Identify: Which component of the atmosphere absorbs the most energy? Which reflects the most?
SHORTWAVE ENERGY BUDGET
Reflected and/or Scattered
By atmosphere and clouds −28
By surface −3 Total −31
Absorbed
By atmosphere and ozone +24
Direct
Diffuse
By surface
Total
Total solar energy input
+45 +69
+100 units
+45 Absorbed by Earth's surface (diffuse + direct)
+25 +20
4.1
SHORTWAVE RADIATION INPUTS AND ALBEDO
Solar energy cascades through the lower atmosphere where it is absorbed, reflected, and scattered. Clouds, atmosphere, and the surface reflect 31% of this insolation back to space. Atmospheric gases and dust and Earth’s surface absorb energy and radiate longwave radiation (as shown in GIA 4.2).
Outgoing shortwave energy reflected from atmosphere, clouds, land, and water, equivalent to Earth’s albedo. [NASA, CERES.]
Reflected shortwave radiation (W·m–2)
0 105 210
Visit the Study Area in MasteringGeographyTM to explore the Earth–atmosphere energy balance.
Visualize: Study geosciences animations of Assess: Demonstrate understanding of the Earth– atmospheric energy balance. atmosphere energy balance (if assigned by instructor).
geosystems in action 4 EARTH–ATMOSPHERE EnERGy BALAnCE