Page 412 - Geosystems An Introduction to Physical Geography 4th Canadian Edition
P. 412
376
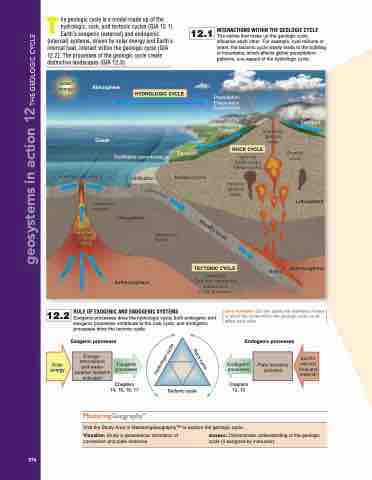
The geologic cycle is a model made up of the hydrologic, rock, and tectonic cycles (GIA 12.1). Earth’s exogenic (external) and endogenic
(internal) systems, driven by solar energy and Earth’s internal heat, interact within the geologic cycle (GIA 12.2). The processes of the geologic cycle create distinctive landscapes (GIA 12.3).
INTERACTIONS WITHIN THE GEOLOGIC CYCLE
The cycles that make up the geologic cycle influence each other. For example, over millions of years, the tectonic cycle slowly leads to the building of mountains, which affects global precipitation patterns, one aspect of the hydrologic cycle.
12 .1
Solar energy
Atmosphere
Ocean
HYDROLOGIC CYCLE
Sea-floor spreading
Upwelling magma
Sediments accumulate
Lithification
Transport
Metamorphism
12 .2
Earth’s heat from radioactive decay
Lithosphere
Asthenosphere
Uppermost mantle
ROLE OF EXOGENIC AND ENDOGENIC SYSTEMS
Exogenic processes drive the hydrologic cycle; both endogenic and exogenic processes contribute to the rock cycle; and endogenic processes drive the tectonic cycle.
Give examples: List two additional examples of ways in which the cycles within the geologic cycle could affect each other.
Precipitation Evaporation Transpiration
Weathering Mass-wasting Erosion
ROCK CYCLE
Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic
Intrusive igneous rocks
TECTONIC CYCLE
Upwelling Sea-floor spreading Subduction Crust formation
Extrusive igneous rocks
Weathering Erosion Transport
Granitic crust
Lithosphere
Asthenosphere
Melting
Energy– atmosphere and water– weather systems activated
Solar energy
Exogenic processes
Exogenic processes
Chapters 14, 15, 16, 17
Endogenic processes
Endogenic processes
Chapters 12, 13
Earth’s internal heat and material
Tectonic cycle
Plate tectonics activated
Visit the Study Area in MasteringGeographyTM to explore the geologic cycle.
Visualize: Study a geosciences animation of Assess: Demonstrate understanding of the geologic convection and plate tectonics. cycle (if assigned by instructor).
S
u
b
d
u
c
t
i
o
n
Basaltic crust
geosystems in action 12The GeoloGic cycle
Rock cycle
Hydrologic cycle