Page 58 - Geosystems An Introduction to Physical Geography 4th Canadian Edition
P. 58
22 Chapter 1 Essentials of Geography
5.
Arctic Circle
4. 2.
Tropic of Capricorn
Antarctic Circle
3.
Arctic: 66.5°N to North Pole Subarctic: 55°N to 66.5°N
Midlatitude: 35°N to 55°N Subtropical: 23.5°N to 35°N
Equatorial and tropical: 23.5°N to 23.5°S
Subtropical: 23.5°S to 35°S Midlatitude: 35°S to 55°S
Subantarctic: 55°S to 66.5°S Antarctic: 66.5°S to South Pole
Tropic of Cancer
Equator
1.
▲Figure 1.15 latitudinal geographic zones. Geographic zones are generalizations that characterise various regions by latitude. Noted cities: 1. Salvador, Brazil; 2. New Orleans, Louisiana; 3. Edinburgh, Scotland; 4. Montreal, Quebec; 5. Barrow, Alaska; see Critical Thinking 1.2.
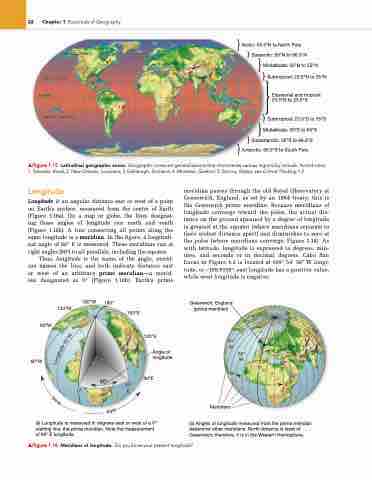
Longitude
Longitude is an angular distance east or west of a point on Earth’s surface, measured from the centre of Earth (Figure 1.16a). On a map or globe, the lines designat- ing these angles of longitude run north and south (Figure 1.16b). A line connecting all points along the same longitude is a meridian. In the figure, a longitudi- nal angle of 60° E is measured. These meridians run at right angles (90°) to all parallels, including the equator.
Thus, longitude is the name of the angle, merid- ian names the line, and both indicate distance east or west of an arbitrary prime meridian—a merid- ian designated as 0° (Figure 1.16b). Earth’s prime
meridian passes through the old Royal Observatory at Greenwich, England, as set by an 1884 treaty; this is the Greenwich prime meridian. Because meridians of longitude converge toward the poles, the actual dis- tance on the ground spanned by a degree of longitude is greatest at the equator (where meridians separate to their widest distance apart) and diminishes to zero at the poles (where meridians converge; Figure 1.14). As with latitude, longitude is expressed in degrees, min- utes, and seconds or in decimal degrees. Cabo San Lucas in Figure 1.2 is located at 109° 549 560 W longi- tude, or –109.9156°; east longitude has a positive value, while west longitude is negative.
Greenwich, England (prime meridian)
60° W
150°W
180°
120°W
150°E
90°W
Angle of 60°W longitude
30° 60°
90°E
(a) Longitude is measured in degrees east or west of a 0° starting line, the prime meridian. Note the measurement of 60° E longitude.
60°
60°
E
0° 30° E E
120°E
0° W
Meridians
E
W 30°E
▲Figure 1.16 Meridians of longitude. Do you know your present longitude?
(b) Angles of longitude measured from the prime meridian determine other meridians. North America is west of Greenwich; therefore, it is in the Western Hemisphere.
L
o
n
g
W
°
i
t
0
u
3
d
e
e
6
d
0
u
t
°
i
E
g
n
o
L
W
e
s
t
t
s
a
E