Page 671 - The Principle of Economics
P. 671
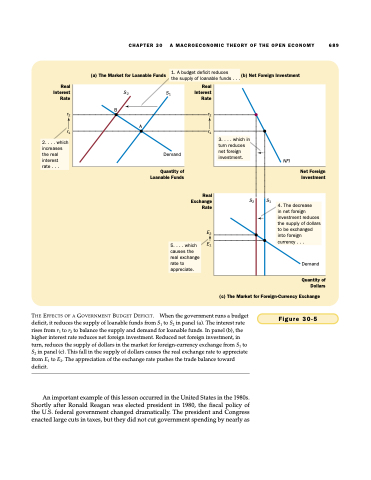
2. . . . which increases the real interest
rate . . .
(a) The Market for Loanable Funds
(b) Net Foreign Investment
CHAPTER 30
A MACROECONOMIC THEORY OF THE OPEN ECONOMY 689
1. A budget deficit reduces
the supply of loanable funds . . .
S2 S1 B
A
Demand
3. . . . which in turn reduces net foreign investment.
NFI
S2
S1
4. The decrease
in net foreign investment reduces the supply of dollars to be exchanged into foreign
currency . . .
Demand
Real Interest Rate
r2 r1
Real Interest Rate
r2 r1
Real Exchange Rate
E2 E1
Quantity of Loanable Funds
Net Foreign Investment
5. . . . which causes the real exchange rate to appreciate.
(c) The Market for Foreign-Currency Exchange
Quantity of Dollars
THE EFFECTS OF A GOVERNMENT BUDGET DEFICIT. When the government runs a budget deficit, it reduces the supply of loanable funds from S1 to S2 in panel (a). The interest rate rises from r1 to r2 to balance the supply and demand for loanable funds. In panel (b), the higher interest rate reduces net foreign investment. Reduced net foreign investment, in turn, reduces the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange from S1 to S2 in panel (c). This fall in the supply of dollars causes the real exchange rate to appreciate from E1 to E2. The appreciation of the exchange rate pushes the trade balance toward deficit.
An important example of this lesson occurred in the United States in the 1980s. Shortly after Ronald Reagan was elected president in 1980, the fiscal policy of the U.S. federal government changed dramatically. The president and Congress enacted large cuts in taxes, but they did not cut government spending by nearly as
Figure 30-5