Page 126 - MYM 2015
P. 126
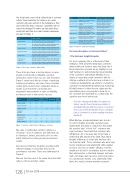
Our study found seven critical cultural traits of customer culture. These determine if a business can create customer advocates and win in the marketplace. They expose the risks that a company’s capabilities will not support its strategy. The names we have given these seven traits and their associated behavior summaries are given in Figure 2.
Traits
Strategic Implication
Business Performance Driver
Customer Insight
Strategic focus on existing customer retention and advocacy.
impacts the ability to drive up customer satisfaction, innovate, new product success and to grow revenues.
Customer Foresight
Strategic focus on new customer acquisition.
Impacts the ability to innovate and develop future revenue streams.
Competitor Insight
Strategic focus on winning market share from existing competitors.
Impacts the ability to grow profits, profit margins and revenues.
Competitor Foresight
Strategic focus on pre-empting new competitors and developing a competitive advantage in emerging markets.
Impacts the ability to innovate and successfully launch new products.
Peripheral Vision
Strategic focus on creation of new products and services and/or creation of new business models.
Impacts the ability to innovate and develop new markets and future revenue streams.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Relevant to all business strategies and a requirement for the effective delivery
of enhanced value for customers.
Impacts the ability to increase customer satisfaction, innovation, new-product success, sales growth, profit growth, and profitability.
Strategic Alignment
Relevant to all business strategies and a requirement for the consistent implementation of strategy with enhanced value for existing and new customers.
Impacts the ability to increase customer satisfaction, innovation, new-product success, sales growth, profit growth, and profitability.
Traits
Behavior Summary
Customer Insight
The extent to which employees monitor, understand, and act on current customer needs and satisfaction.
Customer Foresight
The extent to which employees monitor, understand, and act on potential customer needs and opportunities.
Competitor Insight
The extent to which employees monitor, understand, and respond to current competitor strengths and weaknesses.
Competitor Foresight
The extent to which employees monitor, understand, and respond to new market entrants and potential competitors.
Peripheral Vision
The extent to which employees monitor, understand, and respond to trends in the larger environment (Political, Economic, Social, and Technical).
Cross-Functional Collaboration
The extent to which employees interact, share information, work with, and assist colleagues from other work groups.
Strategic Alignment
The extent to which employees understand, and enact the vision, mission, objectives and strategic direction of the company.
Figure 2: The Seven Customer Culture Traits
These traits also have a decisive impact on sales growth, profit growth, profitability, customer satisfaction, new-product success, and innovation. Figure 3 shows each trait as a driver of particular business performance outcomes. These customer culture traits predict better, sustainable business results. Each trait drives predictable and measurable improvements in sales, profitability, and new-product or new-service success.
Figure 4Customer Culture and Strategy
The Seven Disciplines of Customer Culture20
1.The Customer Insight Discipline
For most companies this is at the heart of their strategies. Think about the many ways customers interact with your business every day. Every one of those interactions presents an opportunity for your staff members to demonstrate their understanding
of the customer’s environment. Whether it is as simple as respecting a retail customer’s time by offering a callback option to resolve a problem or as complex as managing the expectations of enterprise customers by implementing leading-edge technology. All staff behavior is driven by your culture and the expectations placed on everyone to know his or
her customers and treat them in a certain way. The questions you should ask include:
Does the company understand its current cus- tomers’ needs? Does it know how satis ed or dissatis ed they are with its products or services? Does it act on this knowledge? Does it communi- cate to customers its actions resulting from their feedback?
When Westpac, a large Australian bank, decided
to look for insights about why customers were leaving them and going to competitors, they asked the question “why” of both “lost” customers and loyal customers. They found that customers who
left Westpac did so because they did not have a relationship with anyone in the bank. They simply thought of Westpac as a big bank. And they said: “we hate the bank”. Those customers who were loyal had an ongoing personal relationship with a banker and said: “we love our banker”. Westpac took this insight and decided to decentralize decisions back to the bank branches so that bank mangers and loans staff could make quick decisions and provide advice for customersand develop close relationships with them. As a result customer retention increased.
Factors
Customer Satisfaction
Innovation
New Product Success
Profit Growth
Profitability
Sales Revenue Growth
Customer Insight
Customer Foresight
Competitor insight
Competitor Foresight
Peripheral Vision
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Strategic Alignment
Figure 3 Customer Culture Drivers of Business Outcomes
We came to realize that customer culture is a discipline—a set of behaviors and skills that can be developed, refined, and practiced to become habits that lead to better personal and business results.
Also we found that the disciplines are linked with different strategic focuses that drive specific performance outcomes. These are summarized in Figure 4.
We now describe each of the seven disciplines that reflect a strong customer culture.
126 I October 2015