Page 34 - GEORptJul20
P. 34
8.0 Financial & capital markets
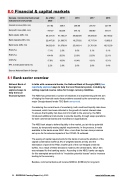
Georgia - Commercial banks lead As of Mar 2019 2018 2017 2016 indicators (end of period) 2020
Interest income (GEL mn)
317.82 339.9 296.86 275.70 227.44
Net profit / loss (GEL mn)
-747.07 953.64 914.72 869.80 679.11
Bank assets (GEL mn)
50,127.75 47,183.37 39,682.98 34,593.50 30,149.32
Bank deposits (GEL mn)
22,447.26 21,390.76 18,273.92 15,717.54 13,662.0
Bank loans (GEL mn)
34,032.43 31,078.64 25,918.14 21,761.90 18,512.30
ROA (%)
-7.1% 2.5% 3.0% 3.1% 3.1%
ROE (%)
-64.4% 20.3% 23.3% 23.3% 22.1%
CAR (%)
17.0% 19.0% 18.4% 19.1% 15.1%
NPL to total gross loans (%)
2.2% 2.6% 2.6% 2.8% 3.4%
Source: National Bank of Georgia
8.1 Bank sector overview
National Bank of Georgia has explored ways to help the local financial system
In talks with commercial banks, the National Bank of Georgia (NBG) has reportedly explored ways to help the local financial system, including by cutting required reserve ratios for foreign currency liabilities.
The NBG has presented a number of initiatives it is implementing with the aim of helping the financial sector face problems caused by the coronavirus crisis, major Georgia-based lender TBC Bank announced.
Considering the current level of uncertainty, both credit and liquidity risks have increased, which has been reflected in the growth of market interest rates.
To ensure that liquidity risk does not limit credit to the economy, the NBG introduced additional instruments to provide liquidity, through swap operations for both commercial banks and microfinance organisations.
The NBG took steps to defend liquidity in the market, put at risk by potential losses, by temporarily easing capital requirements. In the process, it made available to the banks some GEL1.6bn—more than the loan loss provisions set up so far for adverse impacts of the COVID-19 outbreak.
The easing of capital requirements for the banks involves the abolition of the capital conservation buffer (2.5% of weighted assets at risk) and the elimination of part of the Pillar 2 buffer (2/3 of the non-hedged credit risk buffer). As a result of these decisions made by the central bank, GEL1.6bn was released for the banking sector. According to the NBG, banks can apply for this exempted amount both to "neutralise potential losses" and to increase lending to the economy.
Besides, commercial banks will receive $600mn ($188mn) for long-term
34 GEORGIA Country Report July 2020 www.intellinews.com