Page 22 - IRANRptNov19
P. 22
Pakistan, Russia, Oman, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Kuwait, Qatar, Kazakhstan, Armenia, Bahrain and Saudi Arabia.
Based on data published by Iran’s Trade Promotion Organization (TPO), bilateral trade with these countries stood at more than $36.5bn in the last Iranian calendar year, representing around 41% of the country’s total non-oil trade.
Iran plans to launch 15 mega export projects to identify more target markets, according to TPO’s former acting head, Mohammadreza Modoudi.
Iraq, meanwhile, is often the only or obvious source of raw material imports for Iran given the difficulties Iranian producers are having in importing such items from alternative providers who are intimidated by sanctions.
Iraq imported some $6bn of Iranian goods—from air conditioners to agricultural products to car parts—in the year to March, amounting to around 15% of its overall imports last year. Much of the trade is conducted by private Iraqi companies said to have limited exposure in and to the US, and its financial system, and therefore not overly anxious about being sanctioned.
On November 21, Iran announced that smuggled goods with a value of at least $12bn flowed into and out of Iran during the 2017/2018 Persian calendar year (ended March 21).
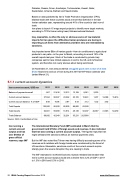
5.1.1 current account dynamics
Iran current account, USD mn
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
Balance of payments overall
-947
21,436
12,213
13,189
8,561
2,233
Current account balance
27,554
58,507
23,362
25,105
15,861
1,237
16,388
15,816
Current account balance: % of GDP
5.66
10.08
3.87
5.43
3.12
0.32
3.92
Total Exports
130,500
95,500
82,000
88,800
63,000
Total Imports
62,661
59,999
51,914
48,138
52,007
40,097
41,945
54,459
Trade Balance
68,692
42,049
32,291
35,231
20,5000
Source: CEIC, Central Bank of Iran
Iran running a current account surplus and has over $100bn of gross official reserves, says IMF
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) estimated in March that the government held $112bn of foreign assets and reserves. It also indicated that Iran was running a current account surplus. The figures imply that Iran might withstand the sanctions without an external payments crisis.
But the IMF also noted that Tehran was having difficulty accessing some of its reserves as its relations with foreign banks were constrained by the threat of US sanctions. Meanwhile, sanctions could cut the current account surplus sharply given the severe disruption they are causing to trade.
The IMF estimated in its World Economic Outlook released last October that Iran’s current account surplus would see a decline from 2.2% of GDP in 2017 to 1.3% in 2018 and 0.3% in 2019.
22 IRAN Country Report November 2019 www.intellinews.com