Page 53 - RPTRusFeb17
P. 53
and a further cut in its share would lead to a loss of control in strategic development decisions, Sokolov said. He added that this could lead to "irreparable damage", especially when the support of Aeroflot is needed as a "base for overall stability in the passenger air transportation".
The privatisation of an additional 4% in Russian diamond major Alrosa is unlikely to happen in 2017, Deputy Finance Minister Alexei Moiseev said on February 16. Last year's successful SPO of 10.9% of Alrosa launched a promising renewed privatisation effort.
Russian Railways will not be privatised until at least 2019, d espite earlier plans to sell part of the rail monopoly along with stakes in other large state companies, Izvestia newspaper quoted First Deputy Prime Minister Igor Shuvalov as saying on February 7. Some major state-owned assets were excluded from the government's recently passed 2017-2019 privatisation programme . Along with Russian Railways, these include Transneft pipe operator, Rostelecom, and Aeroflot, as well as another 10% in oil major Rosneft. Selling stakes in those companies was seen as too risky, an unnamed government official told Vedomosti daily on February 3. Russia's government has confirmed plans to privatise stakes in about 1,800 companies over 2017-2019, although annual revenue estimations vary from a modest RUB60bn (€940mn) to RUB300bn. A stake in shipping major Sovcomflot still earmarked for privatisation will be cut by 25% minus one share, with other major assets including Russia's largest port NSCP (20% planned for sale), as well as further stakes in the Alrosa and Kristall diamond producers.
The privatisation of Russia's second-largest lender VTB Bank will be postponed at least until lifting of the Western sanctions against the country , Reuters reported on February 15, citing Finance Minister Anton Siluanov. The privatisation of VTB is the latest one to be shelved, after the government scaled back its plans for selling state property in 2017-2019. The government planned to cut its stake in VTB from 71% to 25% plus one share, ideally paired with cutting the stake of the central bank in Russia's largest lender Sberbank.
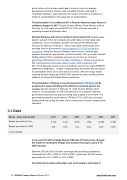
6.2 Debt
Russia - Gross external debt 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Budget: gross debt (LC bn)
4,158 5,343 6,520 7,548 10,299 10,952
Budget: gross debt (% GDP)
8.98 8.95 9.74 10.62 13.22 13.55
source: Rosstat
In its new 2017-2019 strategy Russia’s Ministry of Finance has changed the model for funding the budget and domestic leverage to grow 0.7% GDP annually.
Between 2013 and 2016, Russia’s sovereign debt (excluding guarantees) increased from 8.9% of GDP to 10.9% of GDP. In particular, the OFZ market expanded from 6.3% of GDP to 7.2% of GDP.
According to the approved budget, new local supply is estimated at
53 RUSSIA Country Report February 2017 www.intellinews.com