Page 24 - GEORptFeb19
P. 24
Source: Finance Ministry
6.2 Debt
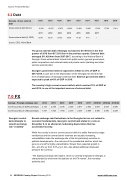
Georgia - Gross external debt
2Q16 3Q16 4Q16 1Q17 2Q17 3Q17 4Q17 1Q18 2Q18
Gross external debt ($ mn)
15,281 15,697 15,872 16,042 16,660 16,881 17,250 17,759 17,411
2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
Gross external debt (% GDP)
32.46 32.53 33.92 35.38 41.28 41.6 /
source: CEIC, World Bank
The gross external debt of Georgia increased to $17,470mn in the first quarter of 2018 from $17,203.5mn in the previous quarter. External debt averaged $11,420.4mn from 2007-2017, according to the National Bank of Georgia. Gross external debt include both public sector (general government, public corporations and national bank) and private sector (banking and other sectors) external debt.
Georgia’s government debt is expected to inflate to 3.5% of GDP in 2017-2019, in part due to the depreciation of the Georgian lari and the high level of dollarisation of Georgia's external debt. External government debt is expected to peak at 43% of GDP in 2018.
The country's high current account deficit, which reached 13% of GDP at end-2016, is one of the important sources of external debt.
7.0 FX
Georgia - Foreign exchange rate
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018 Q1
2018 Q2
2018 Q3
Currency (units per EUR) (average)
2.123
2.209
2.346
2.520
2.617
2.832
3.054
2.918
2.940
Currency (units per USD) (average)
1.651
1.663
1.766
2.270
2.367
2.509
2.485
2.446
2.529
Georgia’s central bank attempts to smooth exchange rate “volatility”
Recent exchange rate fluctuations in the Georgian lari are not related to economic fundamentals, Georgia’s central bank stated in a note on November 6, in an attempt at moderating depreciation that has accelerated recently.
While the country’s chronic current account deficit is safely financed by wage remittances and the central bank’s reserves are actually increasing, vulnerabilities make the exchange rate of the lari particularly sensitive to political developments—the outcome of the presidential election which has gone to a runoff is highly unpredictable. Slower than expected growth in Q3—at 4.0% y/y from 5.5% y/y in Q2—has added additional downward pressure the currency.
“The floating exchange rate regime, which is currently employed in Georgia, is characterised by short-term fluctuations on the FX market”, the monetary authority said.
24 GEORGIA Country Report February 2019 www.intellinews.com