Page 32 - Project Khoka 2
P. 32
THE PROOF-OF-CONCEPT
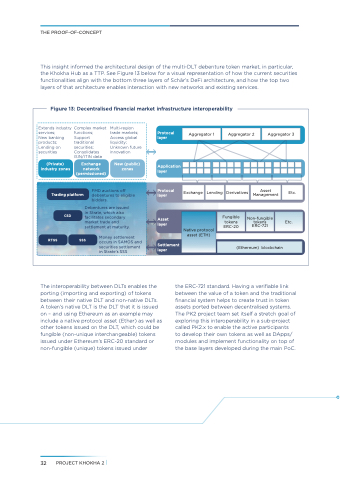
This insight informed the architectural design of the multi-DLT debenture token market, in particular, the Khokha Hub as a TTP. See Figure 13 below for a visual representation of how the current securities functionalities align with the bottom three layers of Schär’s DeFi architecture, and how the top two layers of that architecture enables interaction with new networks and existing services.
Figure 13: Decentralised financial market infrastructure interoperability
Protocal layer
Application layer
Extends industry services;
New banking products; Lending on securities
(Private) industry zones
Complex market functions; Support traditional securities; Consolidates ISIN/ITIN data
Exchange network (permissioned)
Multi-region trade markets; Access global liquidity; Unknown future innovation
New (public) zones
Aggregator 1
Aggregator 2
Aggregator 3
Protocal layer
Asset layer
Settlement layer
Trading platform
CSD
FMD auctions off debentures to eligible bidders.
Debentures are issued in Strate, which also facilitates secondary market trade and settlement at maturity.
Exchange
Fungible tokens ERC-20
Non-fungible tokens ERC-721
Etc.
Native protocol asset (ETH)
Lending
Derivatives
Asset Management
Etc.
RTGS
SSS
Money settlement occurs in SAMOS and securities settlement in Strate’s SSS
The interoperability between DLTs enables the porting (importing and exporting) of tokens between their native DLT and non-native DLTs. A token’s native DLT is the DLT that it is issued on – and using Ethereum as an example may include a native protocol asset (Ether) as well as other tokens issued on the DLT, which could be fungible (non-unique interchangeable) tokens issued under Ethereum’s ERC-20 standard or non-fungible (unique) tokens issued under
(Ethereum) blockchain
the ERC-721 standard. Having a verifiable link between the value of a token and the traditional financial system helps to create trust in token assets ported between decentralised systems. The PK2 project team set itself a stretch goal of exploring this interoperability in a sub-project called PK2.x to enable the active participants
to develop their own tokens as well as DApps/ modules and implement functionality on top of the base layers developed during the main PoC.
32 PROJECT KHOKHA 2