Page 119 - PhD GT
P. 119
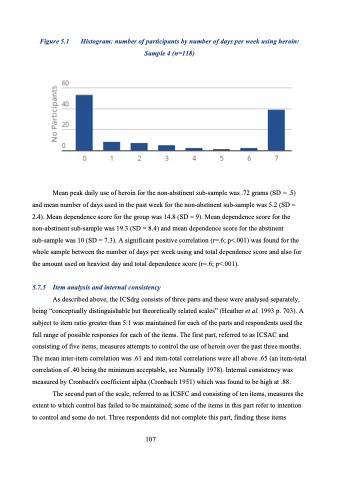
Figure 5.1 Histogram: number of participants by number of days per week using heroin: Sample 4 (n=118)
Mean peak daily use of heroin for the non-abstinent sub-sample was .72 grams (SD = .5) and mean number of days used in the past week for the non-abstinent sub-sample was 5.2 (SD = 2.4). Mean dependence score for the group was 14.8 (SD = 9). Mean dependence score for the non-abstinent sub-sample was 19.3 (SD = 8.4) and mean dependence score for the abstinent sub-sample was 10 (SD = 7.3). A significant positive correlation (r=.6; p<.001) was found for the whole sample between the number of days per week using and total dependence score and also for the amount used on heaviest day and total dependence score (r=.6; p<.001).
5.7.5 Item analysis and internal consistency
As described above, the ICSdrg consists of three parts and these were analysed separately, being “conceptually distinguishable but theoretically related scales” (Heather et al. 1993 p. 703). A subject to item ratio greater than 5:1 was maintained for each of the parts and respondents used the full range of possible responses for each of the items. The first part, referred to as ICSAC and consisting of five items, measures attempts to control the use of heroin over the past three months. The mean inter-item correlation was .61 and item-total correlations were all above .65 (an item-total correlation of .40 being the minimum acceptable, see Nunnally 1978). Internal consistency was measured by Cronbach's coefficient alpha (Cronbach 1951) which was found to be high at .88.
The second part of the scale, referred to as ICSFC and consisting of ten items, measures the extent to which control has failed to be maintained; some of the items in this part refer to intention to control and some do not. Three respondents did not complete this part, finding these items
107