Page 198 - UKZN Proceedings of the Conference Report
P. 198
(CONTINUED)...
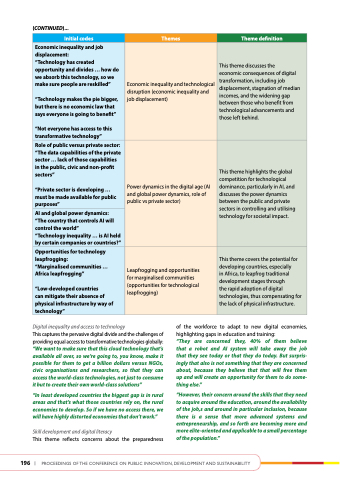
Initial codes
themes
theme definition
economic inequality and job displacement:
“technology has created opportunity and divides ... how do we absorb this technology, so we make sure people are reskilled”
“technology makes the pie bigger, but there is no economic law that says everyone is going to benefit”
“Not everyone has access to this transformative technology”
Economic inequality and technological disruption (economic inequality and job displacement)
This theme discusses the
economic consequences of digital transformation, including job displacement, stagnation of median incomes, and the widening gap between those who benefit from technological advancements and those left behind.
role of public versus private sector: “the data capabilities of the private sector ... lack of those capabilities in the public, civic and non-profit sectors”
“Private sector is developing ... must be made available for public purposes”
Power dynamics in the digital age (AI and global power dynamics, role of public vs private sector)
This theme highlights the global competition for technological dominance, particularly in AI, and discusses the power dynamics between the public and private sectors in controlling and utilising technology for societal impact.
aI and global power dynamics: “the country that controls aI will control the world”
“technology inequality ... is aI held by certain companies or countries?”
opportunities for technology leapfrogging:
“Marginalised communities ... africa leapfrogging”
“Low-developed countries
can mitigate their absence of physical infrastructure by way of technology”
Leapfrogging and opportunities for marginalised communities (opportunities for technological leapfrogging)
This theme covers the potential for developing countries, especially
in Africa, to leapfrog traditional development stages through
the rapid adoption of digital technologies, thus compensating for the lack of physical infrastructure.
Digital inequality and access to technology
This captures the pervasive digital divide and the challenges of providing equal access to transformative technologies globally: “We want to make sure that this cloud technology that’s available all over, so we’re going to, you know, make it possible for them to get a billion dollars versus NGOs, civic organisations and researchers, so that they can access the world-class technologies, not just to consume it but to create their own world-class solutions”
“In least developed countries the biggest gap is in rural areas and that’s what those countries rely on, the rural economies to develop. So if we have no access there, we will have highly distorted economies that don’t work.”
Skill development and digital literacy
This theme reflects concerns about the preparedness
of the workforce to adapt to new digital economies, highlighting gaps in education and training:
“They are concerned they, 40% of them believe that a robot and AI system will take away the job that they see today or that they do today. But surpris- ingly that also is not something that they are concerned about, because they believe that that will free them up and will create an opportunity for them to do some- thing else.”
“However, their concern around the skills that they need to acquire around the education, around the availability of the job,s and around in particular inclusion, because there is a sense that more advanced systems and entrepreneurship, and so forth are becoming more and more elite-oriented and applicable to a small percentage of the population.”
196
| Proceedings of the conference on Public innovation, develoPment and sustainability