Page 131 - Zero Net Energy Case Study Buildings-Volume 2
P. 131
THE EXPLORATORIUM
CASE STUDY NO. 11
ment in such a large building. The radiant heating or cooling is provided via standard plastic tubing distributed throughout the new floor structure and totaling almost 28 miles of hydronic tubing overall.
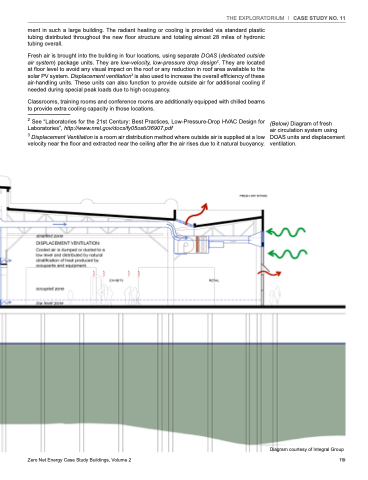
Fresh air is brought into the building in four locations, using separate DOAS (dedicated outside air system) package units. They are low-velocity, low-pressure drop design2. They are located at floor level to avoid any visual impact on the roof or any reduction in roof area available to the solar PV system. Displacement ventilation3 is also used to increase the overall efficiency of these air-handling units. These units can also function to provide outside air for additional cooling if needed during special peak loads due to high occupancy.
Classrooms, training rooms and conference rooms are additionally equipped with chilled beams to provide extra cooling capacity in those locations.
2 See “Laboratories for the 21st Century: Best Practices, Low-Pressure-Drop HVAC Design for Laboratories”, http://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy05osti/36907.pdf
3 Displacement Ventilation is a room air distribution method where outside air is supplied at a low velocity near the floor and extracted near the ceiling after the air rises due to it natural buoyancy.
(Below) Diagram of fresh
air circulation system using DOAS units and displacement ventilation.
Zero Net Energy Case Study Buildings, Volume 2
119
Diagram courtesy of Integral Group