Page 370 - statbility for masters and mates
P. 370
358 Ship Stability for Masters and Mates
and
So
Stress E Ry f E Ry
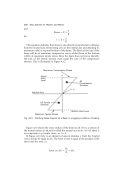
This equation indicates that stress is also directly proportional to distance from the neutral axis, stress being zero at the neutral axis and attaining its maximum value at top and bottom of the beam. The ®bres at the top of the beam will be at maximum compressive stress whilst those at the bottom will be at maximum tensile stress. Since the beam does not move laterally, the sum of the tensile stresses must equal the sum of the compressive stresses. This is illustrated in Figure 43.2.
Fig. 43.2. Bending Stress diagram for a Beam in a sagging condition of loading.
Figure 43.3 shows the cross-section of the beam at ab. NA is a section of the neutral surface at ab and is called the neutral axis at ab. At NA there is no compressive or tensile stress, so f 0.
In Figure 43.3 bdy is an element of area at distance y from the Neutral Axis. Let bdy be equal to dA. The force on dA is equal to the product of the stress and the area. i.e.
Force on dA Ey dA. R