Page 7 - Alaska A & P Primer
P. 7
Human anatomy is the scientific study of the body’s structures. In the past, anatomy has primarily been studied via observing injuries, and later by the dissection of anatomical structures of cadavers, but in the past century, computer-assisted imaging techniques have allowed clinicians to look inside the living body. Human physiology is the scientific study of the chemistry and physics of the structures of the body. Physiology explains how the structures of the body work together to maintain life. It is difficult to study structure (anat- omy) without knowledge of function (physiology). The two disciplines are typically studied together because form and function are closely related in all living things.
1.2 | Structural Organization of the Human Body
1.2 OBJECTIVES
1. Describe the structure of the human body in terms of six levels of organization
2. List the eleven organ systems of the human body and identify at least one organ and one major function of each
This content is available for free at https://cnx.org/content/col11496/1.7
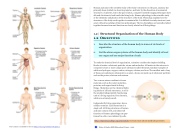
To study the chemical level of organization, scientists consider the simplest building blocks of matter: subatomic particles, atoms and molecules. All matter in the universe is composed of one or more unique pure substances called elements, familiar examples of which are hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, calcium, and iron. The smallest unit of any of these pure substances (elements) is an atom. Atoms are made up of subatomic particles such as the proton, electron and neutron.
Two or more atoms combine to form a molecule, such as the water molecules, proteins, and sugars found in living things. Molecules are the chemical build- ing blocks of all body structures. A cell is the smallest independently functioning unit of a living organism. Even bacteria, which are extremely small,
independently-living organisms, have a cellular structure. Each bacterium is a single cell. All living structures of human anatomy contain cells, and almost all functions of human physiology are per- formed in cells or are initiated by cells.
(http://Openstaxcollege.org/l/metabolic) to learn more about metabolic processes.
State of Alaska EMS Education Primer - 2016 6