Page 736 - Algebra 1
P. 736
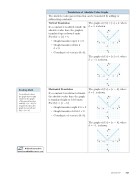
Translations of Absolute-Value Graphs
The absolute-value parent function can be translated by adding or subtracting constants.
Vertical Translation
If a constant k is added outside the absolute-value bars, the graph is translated up or down k units.
For f(x) = ⎢x + k:
• Graph translates up if k > 0. • Graph translates down if
k < 0.
• Coordinate of vertex is (0, k).
The graph of f(x) = ⎢x + k, where k = 1, is shown.
4
x
-8
-4
4
8
-4
-8
The graph of f(x) = ⎢x + k, where k = -1, is shown.
y
8
y
8
4
x
-8
-4
Horizontal Translation
If a constant h is subtracted inside the absolute-value bars, the graph is translated right or left h units. For f(x) = ⎢x - h :
• Graph translates right if h > 0. • Graph translates left if h < 0.
• Coordinate of vertex is (h, 0).
y
4
8
-4
-8
The graph of f(x) = ⎢x - h , where h = 1, is shown.
8
4
x
-8
-4
4
8
-4
-8
The graph of f(x) = ⎢x - h , where h = -1, is shown.
y
8
4
x
-8
-4
-4
-8
4
8
Reading Math
For positive h values, the graph moves right relative to the graph of the parent function and f(x) = ⎢x - h . For negative h values, the graph moves left and f(x) = ⎢x + h .
Online Connection www.SaxonMathResources.com
Lesson 107 721