Page 424 - Canadian BC Science 9
P. 424
Chapter
11
Prepare Your Own Summary
In this chapter, you learned about several components of space. Create your own summary of the key ideas from this chapter. You may include graphic organizers or illustrations with your notes. (See Science Skill 12 for help with using graphic organizers.) Use the following headings to organize your notes:
1. Life Cycles of Stars
2. Analyzing the Composition of Stars
3. The Solar System
4. Measuring Distances in Space
Checking Concepts
1. What is the process that creates energy in stars?
2. At which stage in a star’s life will it turn into a supernova?
3. How old is the solar system?
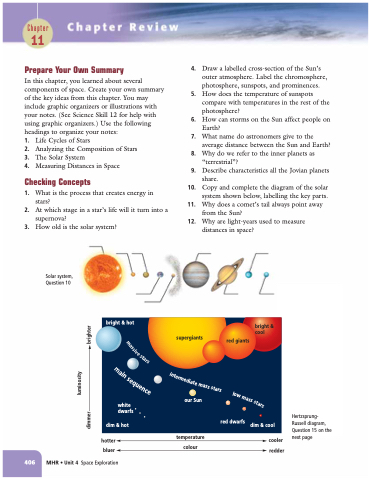
Solar system, Question 10
4. Draw a labelled cross-section of the Sun’s outer atmosphere. Label the chromosphere, photosphere, sunspots, and prominences.
5. How does the temperature of sunspots compare with temperatures in the rest of the photosphere?
6. How can storms on the Sun affect people on Earth?
7. What name do astronomers give to the average distance between the Sun and Earth?
8. Why do we refer to the inner planets as “terrestrial”?
9. Describe characteristics all the Jovian planets share.
10. Copy and complete the diagram of the solar system shown below, labelling the key parts.
11. Why does a comet’s tail always point away from the Sun?
12. Why are light-years used to measure distances in space?
bright & hot
bright & cool
white dwarfs
dim & hot
our Sun
red giants
red dwarfs
dim & cool
supergiants
hotter bluer
temperature colour
cooler redder
Hertzsprung- Russell diagram, Question 15 on the next page
406 MHR • Unit 4 Space Exploration
m
a
s
s
i
v
e
s
t
a
s
m
a
i
i
n
n
t
e
r
m
s
r
e
e
d
i
a
q
t
e
ma
u
a st
ss
e
n
r
s
c
e
l
o
w
m
a
s
s
s
t
a
r
s
dimmer
brighter
luminosity