Page 250 - Sociology and You
P. 250
220 Unit 2 Culture and Social Structures
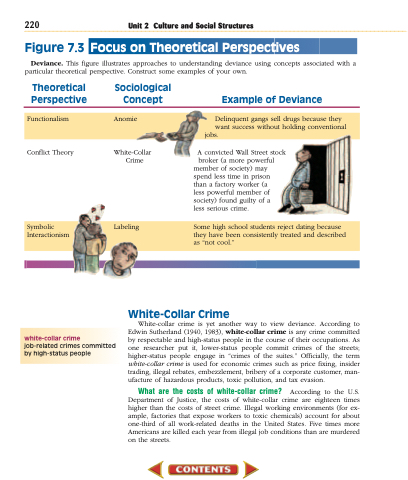
Figure 7.3 Focus on Theoretical Perspectives
Deviance. This figure illustrates approaches to understanding deviance using concepts associated with a particular theoretical perspective. Construct some examples of your own.
Theoretical Perspective
Conflict Theory
Sociological Concept
White-Collar Crime
Example of Deviance
A convicted Wall Street stock broker (a more powerful
member of society) may spend less time in prison than a factory worker (a less powerful member of society) found guilty of a less serious crime.
Functionalism Anomie Delinquent gangs sell drugs because they want success without holding conventional
jobs.
Symbolic Labeling Some high school students reject dating because Interactionism they have been consistently treated and described
as “not cool.”
white-collar crime
job-related crimes committed by high-status people
White-Collar Crime
White-collar crime is yet another way to view deviance. According to Edwin Sutherland (1940, 1983), white-collar crime is any crime committed by respectable and high-status people in the course of their occupations. As one researcher put it, lower-status people commit crimes of the streets; higher-status people engage in “crimes of the suites.” Officially, the term white-collar crime is used for economic crimes such as price fixing, insider trading, illegal rebates, embezzlement, bribery of a corporate customer, man- ufacture of hazardous products, toxic pollution, and tax evasion.
What are the costs of white-collar crime? According to the U.S. Department of Justice, the costs of white-collar crime are eighteen times higher than the costs of street crime. Illegal working environments (for ex- ample, factories that expose workers to toxic chemicals) account for about one-third of all work-related deaths in the United States. Five times more Americans are killed each year from illegal job conditions than are murdered on the streets.