Page 26 - Natl Into R Literature Brochure 48pp
P. 26
GRADES 3–5 OVERVIEW
Inspire a love of reading with engaging, topically
related text sets!
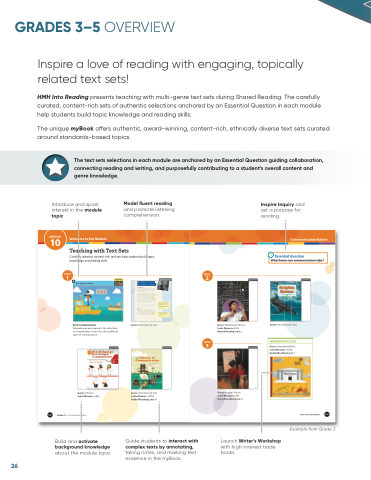
HMH Into Reading presents teaching with multi-genre text sets during Shared Reading. The carefully curated, content-rich sets of authentic selections anchored by an Essential Question in each module help students build topic knowledge and reading skills.
The unique myBook o ers authentic, award-winning, content-rich, ethnically diverse text sets curated around standards-based topics.
The text sets selections in each module are anchored by an Essential Question guiding collaboration, connecting reading and writing, and purposefully contributing to a student’s overall content and genre knowledge.
Introduce and interest in the topic.
DO NOT EDIT--Changes must be made th CorrectionKey=NL-A
ark
dule
ugh “File info”
Model uent reading
and promote listening comprehension.
Inspire Inquiry and set a purpose for reading.
DO NOT EDIT--ChaDngOeNs OmTuEstDbITe--mChadanegthesromuugsht“bFieleminafdoe” through “File info” CorrectionKey=NLC-AorrectionKey=NL-A
4re_te_10_ts.indd
196
4re_te_51/02_/t2s0.i1n8dd6:5159:740 AM
5/2/2018
6:55:50 AM
Example from Grade 3
26
Build and activate background knowledge about the module topic.
Guide students to interact with complex texts by annotating, taking notes, and marking text evidence in the myBook.
Launch Writer’s Workshop with high-interest trade books.
MODULE 10
Welcome to the Module
Teaching with Text Sets
Carefully selected, content-rich text sets help students build topic knowledge and reading skills.
WEEK 1
DCoOrrNeOctTioEnDKIeTy--=CThXa-nAges must be made through “File info”
READ-ALOUD TEXT
The Unbroken Code of the Navajo Code Talkers by CATHERINE RIPLEY
World War II began in September 1939 when Germany, under the control of Adolf Hitler, invaded Poland. The United States entered the war on December 7, 1941, when Japan bombed the US Navy in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. At this point, Japan had formed an alliance with Germany.
It’s August 7, 1942, in the middle of World War II, and a huge battle is unfolding on Guadalcanal Island in the Pacific Ocean. Hidden in the steamy jungle, two Japanese soldiers watch American Marines roll out wire from one battle patrol to the next. In the distance, gunfire rattles and bombs blast. When the Americans are gone, the soldiers creep out to tap into the newly laid communication line. Both understand English well and hope to eavesdrop on what the Americans are planning. The first Japanese soldier listens, and a look of surprise crosses his face. He hears a sing-song “mumbling” and some throaty gurgles and clicks. The second soldier also listens and recognizes that it isn’t English. It’s like nothing they’ve ever heard before!
What do they hear? Two Navajo code talkers on their field telephones. The code talkers enabled Americans to communicate secretly and speedily in the heat of battle and were critical to winning the war in the Pacific. Their code was never broken by the Japanese. A
Why Navajo?
The idea for using Navajo code talkers was suggested by the son of a missionary, Philip Johnston, who had grown up on the Navajo Reservation. Johnston knew that Navajo was an unusual language that few people outside the tribe could understand, and he also knew how important it was for the Marines to be able to communicate quickly without using cumbersome decoding machines or codebooks that could fall into enemy hands. B
COMMUNICATION
GET CURIOUS VIDEO
Born to Communicate
Students view and respond to the video Born to Communicate to learn more about different types of communication.
A
B
READ ALOUD
What was so strange about the message tchoemJmapuaniecasetiosonldlinieer?s(hTehaerladnogvueargtehweasn’t like anything they’d ever heard before.) DOK 1 What were the soldiers actually hearing? (NTahveasjionlga-nsognugagmeu.)mbling and clicking of thDeOK 2 TEKS 4.6G, 4.7C, 4.9D(i); ELPS 2G, 2H, 2I
What made the Navajo language perfect f(Foerwcopemompleuonuictsaidtientgheserecsrertvamtieosnskangeewsi?t. There was no need for cumbersome codebooks.)
308
myNotes
How Technology Read Has Changed
Short
Genre: Timeline Lexile Measure: 880L
Communication
Timeline of Communications Technology
This timeline shows when important communication devices became popular in the United States.
Tlohneg tdeislteagnrceaspohvseernwt imreess.sages
ToeultemgreapsshagoepseirnatMoorsrsteapcpoedde, a sytasntedmfoorfledtotetsrsa.nd dashes that
1850s
Ainvftenrteted,lepveiospiolencwoualsd see eTevelenvtisioasntbhreoyuhgahptppeenoepdl.e tmoogemtheenrtstoinwhistntoersys. important
1950s
Ianrtahdei1o9f2o0rst,heevierrliyvoingerwooanmte. d Fhaemarilaiens egwatsheoreednaterortuanindmitetnot
1860s
Tcahlledtethlepghreoantesht ainsvbeenetinon of tlohneg1e9rthacdenttourbye. Pineothpelesnamo e room to talk to one another! 1870s
1920s
Bpeofoprle twhreotyepletwteristaenrd,
oTthheetrydpoecwurmiterntms abdyehwanrdit.ing
apubboliockatoiornomthuecrhlefansgttehry. broadcast.
my BOOK
my BOOK myNotes
311
(2cConletainrnuende)w lEaNngGuLaIgSeHsLtAruNcGtuUreAsG/eExPpRreOssFiIoCnIsE/NvCocYaSbTuAlaNryD;A2RGDuSnd1erDstsapnedakmuesainigngle/amrnainingpsotrinates/gdiest;a1ilsEoinf tsepronkaelinzelanegwuabgaes;ic2/Hacuanddeemrsictalnandguage; implicit ideas/information in spoken language; 2I demonstrate listening comprehension of spoken English.
Genre: Informational Text
DO NOT EDIT--Changes must be made through “File info” CorrectionKey=TX-A
The History of Communication illustrations by Danny Schlitz
Genre: Informational Text Lexile Measure: 1070L Guided Reading Level: N
Listening Comprehension
TEKS 4.6G, 4.7C, 4.9D(i); ELPS 2G, 2H, 2I
DOK 1
T239
T196 Module 10 • Communication Nation
Communication Nation
CorrectionKey=TX-A
Essential Question pW_hbaotdfoy-rqmusecsatinocnommunication take?
WEEK 2
WEEK 3
DO NOT EDIT--Changes must be made through "File info"
Genre: Narrative Nonfiction Lexile Measure: 850L Guided Reading Level: L
DO NOT EDIT--Changes must be made through “File info”
Genre: Realistic Fiction Lexile Measure: 630L Guided Reading Level: O
my BOOK
my BOOK
DO NOT EDIT--Changes must be made through “File info” m
Genre: Informational Video
B
m
K
y
y
B
O
O
O
O
K
CorrectionKey=TX-A
m
by Charnan Simon
yNotes
331
Correctionkey=TX-A
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
Do
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
l
l
l
l
l
l
lp
p
p
p
p
p
ph
h
h
h
h
h
i
i
i
i
D
e
n
i
i
in
n
n
n
Di
D
in
n
r
D
D
D
D
D
i
i
i
i
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
e
e
e
e
e
r
r
r
r
from National Geographic Kids
myNotes
339
myNotes
345
Welcome to the Module T197
WRITING FOCAL TEXT
Genre: Informational Text Lexile Measure: 1070L Guided Reading Level: T
sp
mo
ro
story by Sun Yung Shin illustrated by Kim Cogan