Page 279 - MATHEMATICS COURSE FOR SECONDARY SCHOOLS BOOK 2
P. 279
19.
20.
(a) JK is formed by the points J (-10, -3) and K (5, 9). Determine vector JK in the
EXAMPLE 6
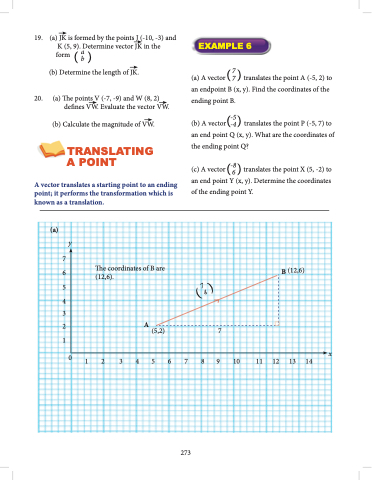
(a) A vector ( 7 ) translates the point A (-5, 2) to an endpoint B (x, y). Find the coordinates of the ending point B.
-5
(b) A vector(-4 ) translates the point P (-5, 7) to
an end point Q (x, y). What are the coordinates of the ending point Q?
(c) A vector (-8 ) translates the point X (5, -2) to 6
an end point Y (x, y). Determine the coordinates of the ending point Y.
B (12,6)
f o r m ( ab )
(b) Determine the length of JK.
(a) The points V (-7, -9) and W (8, 2) defines VW. Evaluate the vector VW.
(b) Calculate the magnitude of VW.
TRANSLATING A POINT
A vector translates a starting point to an ending point; it performs the transformation which is known as a translation.
(a)
y
7
6
5
4 3
2 1
0
The coordinates of B are (12,6).
A (5,2)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
273
7
x
( 74 )