Page 301 - MATHEMATICS COURSE FOR SECONDARY SCHOOLS BOOK 2
P. 301
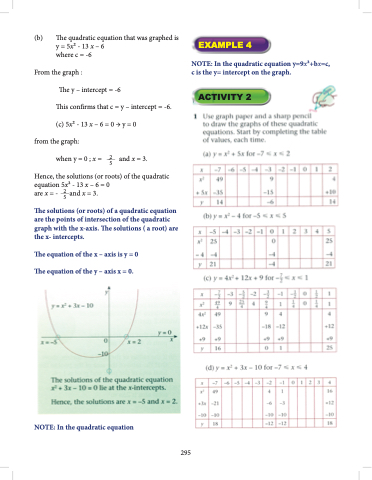
(b) The quadratic equation that was graphed is y = 5x2 - 13 x – 6
where c = -6 From the graph :
The y – intercept = -6
This confirms that c = y – intercept = -6. (c) 5x2 - 13 x – 6 = 0 → y = 0
from the graph:
when y = 0 ; x = - and x = 3.
Hence, the solutions (or roots) of the quadratic equation 5x2 - 13 x – 6 = 0
are x = - 25 and x = 3.
The solutions (or roots) of a quadratic equation are the points of intersection of the quadratic graph with the x-axis. The solutions ( a root) are the x- intercepts.
The equation of the x – axis is y = 0 The equation of the y – axis x = 0.
EXAMPLE 4
NOTE: In the quadratic equation y=9x2+bx=c, c is the y= intercept on the graph.
ACTIVITY 2
NOTE: In the quadratic equation
2 5
295