Page 16 - demo
P. 16
INTRODUCTION
for gasoline engines. Although a fair percentage of methanol can be added to gasoline, there
are several problems such as higher vapour pressure, separation in presence of water etc.
Therefore, generally less than 3 % methanol is added with gasoline for use with unmodified
gasoline engines. In addition to blending with gasoline, methanol is widely used as a clean
liquefied hydrogen carrier for fuel cells. Fuel cells which directly use methanol also exist, where
an on-line reformer is not required for hydrogen generation.
On the other hand, DME has a much higher Cetane No. (55 to 60), which makes it suitable for
diesel engines. It is infinitely soluble with diesel, at least at ambient temperature, and even at
below 0°C, 30% DME remains dissolved. Therefore, blending of up to 30% DME with diesel is
feasible without any major modification of engines. Pure DME is also possible to be used as
fuel, using pressurized fuel storage and delivery system, but this requires major modifications
in the diesel engine.
Regarding emission from DME or DME diesel blends as fuel, there is reduction in smoke and
particulate matter, but no significant benefit on GHG emission unless DME is produced from
renewable resources.
As compared to fossil based transportation fuels, where completely sulfur free fuel is difficult
or expensive to produce, both methanol and DME could easily be produced as zero sulfur fuel.
Since the current growth in use of both methanol and DME are for their use in transportation
fuels, the specification is required to be compatible with the engine. For production of DME
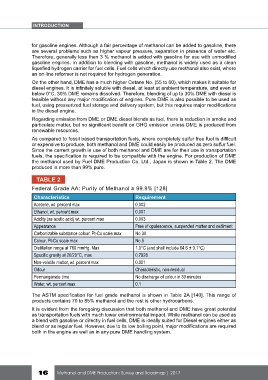
the methanol used by Fuel DME Production Co. Ltd., Japan is shown in Table 2. The DME
produced is more than 99% pure.
TABLE 2
Federal Grade AA: Purity of Methanol ≥ 99.9% [128]
Characteristics Requirement
Acetone, wt. percent max 0.002
Ethanol, wt. percent max 0.001
Acidity (as acetic acid) wt. percent max 0.003
Appearance Free of opalescence, suspended matter and sediment
Carbonizable substance colour, Pt-Co scale max No.30
Colour, Pt-Co scale max No.5
Distillation range at 760 mmHg. Max 1.0°C (and shall include 64.6 ± 0.1°C)
Specific gravity at 20/20°C, max 0.7928
Non-volatile matter, wt. percent max 0.001
Odour Characteristic, non-residual
Permanganate time No discharge of colour in 30 minutes
Water, wt. percent max 0.1
The ASTM specification for fuel grade methanol is shown in Table 2A [140]. This range of
products contains 70 to 85% methanol and the rest is other hydrocarbons.
It is evident from the foregoing discussion that both methanol and DME have great potential
as transportation fuels with much lower environmental impact. While methanol can be used as
a blend with gasoline or directly in fuel cells, DME is ideally suited for Diesel engines either as
blend or as regular fuel. However, due to its low boiling point, major modifications are required
both in the engine as well as in any pure DME handling system.
16 Methanol and DME Production: Survey and Roadmap | 2017