Page 36 - LASERS & IPLS IN MEDICAL/AESTHETIC APPLICATIONS
P. 36
Basic IPL Design
Chapter 1 – Fundamentals of Medical/Aesthetic Lasers and IPLs v1.1
Compared with lasers, IPL systems are fairly simple devices – see figure 16.
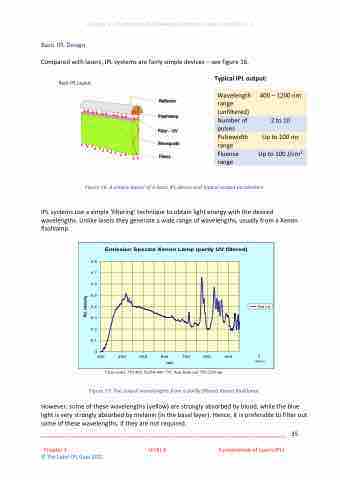
Basic IPL Layout
Typical IPL output:
0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1
0
Rel int.
1200nm
350 450 550
650 750
nm
850 950
Reflector Flashlamp
Filter Waveguide
Filters
Wavelength range (unfiltered) Number of pulses Pulsewidth range Fluence range
400 – 1200 nm
2 to 10
Up to 100 ms Up to 100 J/cm2
Rel. intensity
Ultra-violet 350-400, Visible 400-750, Near Infra-red 750-1200 nm
-
UV
Figure 16: A simple layout of a basic IPL device and typical output parameters
IPL systems use a simple ‘filtering’ technique to obtain light energy with the desired wavelengths. Unlike lasers they generate a wide range of wavelengths, usually from a Xenon flashlamp.
Emission Spectra Xenon Lamp (partly UV filtered)
Figure 17: The output wavelengths from a partly filtered Xenon flashlamp.
However, some of these wavelengths (yellow) are strongly absorbed by blood, while the blue light is very strongly absorbed by melanin (in the basal layer). Hence, it is preferable to filter out some of these wavelengths, if they are not required.
________________________________________________________________________ 35
Chapter 1 LEVEL A Fundamentals of Lasers/IPLs
© The Laser-IPL Guys 2021