Page 8 - Marine Magnetometer Processing
P. 8
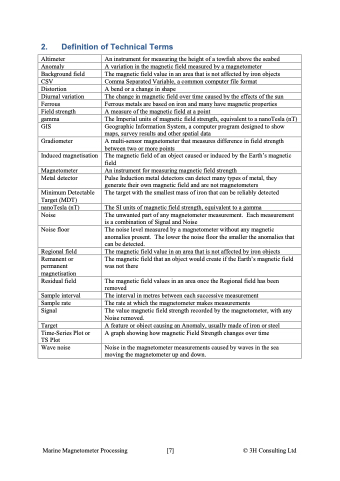
2. Definition of Technical Terms Altimeter Anomaly Background field CSV Distortion Diurnal variation Ferrous Field strength gamma GIS Gradiometer Induced magnetisation Magnetometer Metal detector Minimum Detectable Target (MDT) nanoTesla (nT) Noise Noise floor Regional field Remanent or permanent magnetisation Residual field Sample interval Sample rate Signal Target Time-Series Plot or TS Plot Wave noise An instrument for measuring the height of a towfish above the seabed A variation in the magnetic field measured by a magnetometer The magnetic field value in an area that is not affected by iron objects Comma Separated Variable, a common computer file format A bend or a change in shape The change in magnetic field over time caused by the effects of the sun Ferrous metals are based on iron and many have magnetic properties A measure of the magnetic field at a point The Imperial units of magnetic field strength, equivalent to a nanoTesla (nT) Geographic Information System, a computer program designed to show maps, survey results and other spatial data A multi-sensor magnetometer that measures difference in field strength between two or more points The magnetic field of an object caused or induced by the Earth’s magnetic field An instrument for measuring magnetic field strength Pulse Induction metal detectors can detect many types of metal, they generate their own magnetic field and are not magnetometers The target with the smallest mass of iron that can be reliably detected The SI units of magnetic field strength, equivalent to a gamma The unwanted part of any magnetometer measurement. Each measurement is a combination of Signal and Noise The noise level measured by a magnetometer without any magnetic anomalies present. The lower the noise floor the smaller the anomalies that can be detected. The magnetic field value in an area that is not affected by iron objects The magnetic field that an object would create if the Earth’s magnetic field was not there The magnetic field values in an area once the Regional field has been removed The interval in metres between each successive measurement The rate at which the magnetometer makes measurements The value magnetic field strength recorded by the magnetometer, with any Noise removed. A feature or object causing an Anomaly, usually made of iron or steel A graph showing how magnetic Field Strength changes over time Noise in the magnetometer measurements caused by waves in the sea moving the magnetometer up and down. Marine Magnetometer Processing \[7\] © 3H Consulting Ltd