Page 100 - RoadCem Manual - PCT BV
P. 100
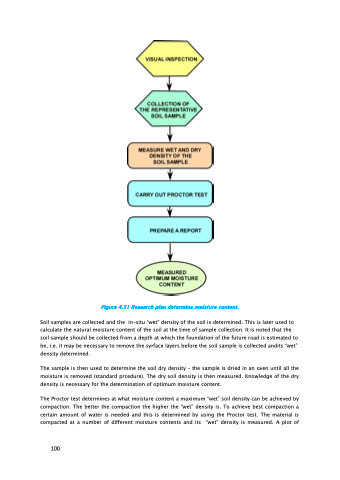
Figure 4.51 Research plan determine moisture content.
Soil samples are collected and the in-situ “wet” density of the soil is determined. This is later used to calculate the natural moisture content of the soil at the time of sample collection. It is noted that the soil sample should be collected from a depth at which the foundation of the future road is estimated to be, i.e. it may be necessary to remove the syrface layers before the soil sample is collected andits “wet” density determined.
The sample is then used to determine the soil dry density – the sample is dried in an oven until all the moisture is removed (standard prcedure). The dry soil density is then measured. Knowledge of the dry density is necessary for the determination of optimum moisture content.
The Proctor test determines at what moisture content a maximum “wet” soil density can be achieved by compaction. The better the compaction the higher the “wet” density is. To achieve best compaction a certain amount of water is needed and this is determined by using the Proctor test. The material is compacted at a number of different moisture contents and its “wet” density is measured. A plot of
100