Page 73 - RoadCem Manual - PCT BV
P. 73
During the visual inspection one estimates how many tests (must) be made. In most casess when dealing with polluted soils it is a legal requirement to determine the chemical composition and to prove that the relevant substances that are present in the in-situ material can be immobilized.
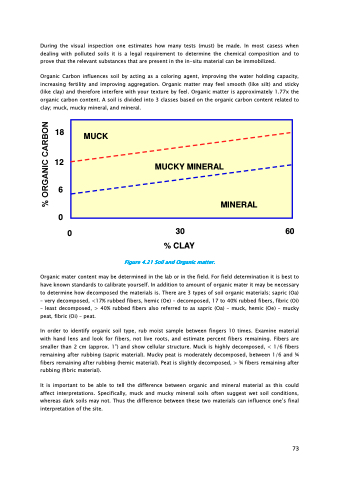
Organic Carbon influences soil by acting as a coloring agent, improving the water holding capacity, increasing fertility and improving aggregation. Organic matter may feel smooth (like silt) and sticky (like clay) and therefore interfere with your texture by feel. Organic matter is approximately 1.77x the organic carbon content. A soil is divided into 3 classes based on the organic carbon content related to clay; muck, mucky mineral, and mineral.
18
12 6 0
0
30 60 % CLAY
MUCK
MUCKY MINERAL
MINERAL
Figure 4.21 Soil and Organic matter.
Organic mater content may be determined in the lab or in the field. For field determination it is best to have known standards to calibrate yourself. In addition to amount of organic mater it may be necessary to determine how decomposed the materials is. There are 3 types of soil organic materials; sapric (Oa) – very decomposed, <17% rubbed fibers, hemic (Oe) – decomposed, 17 to 40% rubbed fibers, fibric (Oi) – least decomposed, > 40% rubbed fibers also referred to as sapric (Oa) – muck, hemic (Oe) – mucky peat, fibric (Oi) – peat.
In order to identify organic soil type, rub moist sample between fingers 10 times. Examine material with hand lens and look for fibers, not live roots, and estimate percent fibers remaining. Fibers are smaller than 2 cm (approx. 1”) and show cellular structure. Muck is highly decomposed, < 1/6 fibers remaining after rubbing (sapric material). Mucky peat is moderately decomposed, between 1/6 and 3⁄4 fibers remaining after rubbing (hemic material). Peat is slightly decomposed, > 3⁄4 fibers remaining after rubbing (fibric material).
It is important to be able to tell the difference between organic and mineral material as this could affect interpretations. Specifically, muck and mucky mineral soils often suggest wet soil conditions, whereas dark soils may not. Thus the difference between these two materials can influence one’s final interpretation of the site.
73