Page 97 - RoadCem Manual - PCT BV
P. 97
Extremely Low Very Low Low Moderate High
Very High Extremely High
Processing results
< 0.01 0.01 to <0.1 0.1 to <1 1 to <2
2 to <4
4 to <9 >8
Table 4.8 Penetration Resistance.
PENETRATION RESISTANCE
Penetration Resistance Class
Criteria : Penetration Resistance (MPa)
The thickness of the foundation is determined based on the minimum bearing strength value of various locations on the road.
4.2.9 Ground water level
The ground water level has an effect on the frost-thaw behaviour of the sub-base and the capillary effect on it. When the water level is too high the sub-base has a lower bearing strength.There is also chance of frost-thaw damage in the sub-base.To avoid this in a traditional construction a drainage or a thicker foundation is necessary. With the use of RoadCem the need for drainage is reduced but is not eliminated and the extent will depend on the actual consditions in the field.
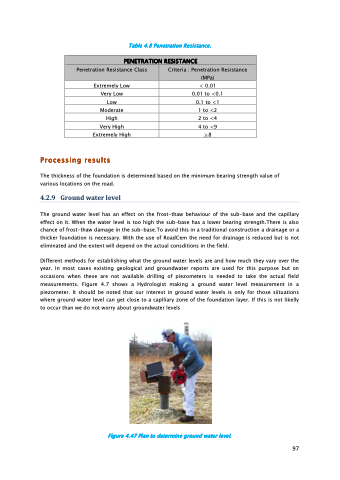
Different methods for establishing what the ground water levels are and how much they vary over the year. In most cases existing geological and groundwater reports are used for this purpose but on occasions when these are not available drilling of piezometers is needed to take the actual field measurements. Figure 4.7 shows a Hydrologist making a ground water level measurement in a piezometer. It should be noted that our interest in ground water levels is only for those siituations where ground water level can get close to a caplliary zone of the foundation layer. If this is not likelly to occur than we do not worry about groundwater levels
Figure 4.47 Plan to determine ground water level.
97