Page 34 - Demo
P. 34
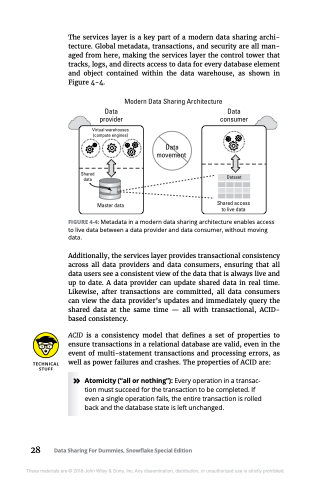
The services layer is a key part of a modern data sharing archi- tecture. Global metadata, transactions, and security are all man- aged from here, making the services layer the control tower that tracks, logs, and directs access to data for every database element and object contained within the data warehouse, as shown in Figure 4-4.
FIGURE 4-4: Metadata in a modern data sharing architecture enables access to live data between a data provider and data consumer, without moving data.
Additionally, the services layer provides transactional consistency across all data providers and data consumers, ensuring that all data users see a consistent view of the data that is always live and up to date. A data provider can update shared data in real time. Likewise, after transactions are committed, all data consumers can view the data provider’s updates and immediately query the shared data at the same time — all with transactional, ACID- based consistency.
ACID is a consistency model that defines a set of properties to ensure transactions in a relational database are valid, even in the event of multi-statement transactions and processing errors, as well as power failures and crashes. The properties of ACID are:
» Atomicity (“all or nothing”): Every operation in a transac- tion must succeed for the transaction to be completed. If even a single operation fails, the entire transaction is rolled back and the database state is left unchanged.
28 Data Sharing For Dummies, Snowflake Special Edition
These materials are © 2018 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Any dissemination, distribution, or unauthorized use is strictly prohibited.