Page 22 - Proof no 3
P. 22
2.
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 31 DECEMBER 2018 (CONTINUED)
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
(a) Basis of preparation (continued)
New standards, amendments and interpretations adopted by the Group (continued)
Amendments to IFRS 4 – Applying IFRS 9 Financial Instruments with IFRS 4 Insurance Contracts (continued)
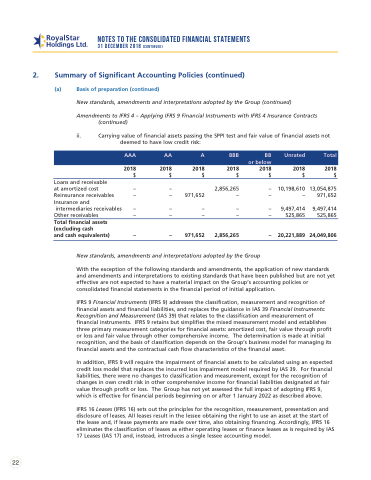
ii. Carrying value of financial assets passing the SPPI test and fair value of financial assets not deemed to have low credit risk:
AAA AA A BBB BB Unrated Total or below
2018 2018 2018 2018 2018 2018 2018
$$$$$$$
Loans and receivable
at amortized cost – – Reinsurance receivables – – Insurance and
intermediaries receivables – – Other receivables – – Total financial assets
(excluding cash
and cash equivalents) – –
2,856,265 – 10,198,610 971,652 – – –
–– – 9,497,414
–– – 525,865
971,652 2,856,265 – 20,221,889
13,054,875 971,652
9,497,414 525,865
24,049,806
22
New standards, amendments and interpretations adopted by the Group
With the exception of the following standards and amendments, the application of new standards and amendments and interpretations to existing standards that have been published but are not yet effective are not expected to have a material impact on the Group’s accounting policies or consolidated financial statements in the financial period of initial application.
IFRS 9 Financial Instruments (IFRS 9) addresses the classification, measurement and recognition of financial assets and financial liabilities, and replaces the guidance in IAS 39 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement (IAS 39) that relates to the classification and measurement of financial instruments. IFRS 9 retains but simplifies the mixed measurement model and establishes three primary measurement categories for financial assets: amortized cost, fair value through profit or loss and fair value through other comprehensive income. The determination is made at initial recognition, and the basis of classification depends on the Group’s business model for managing its financial assets and the contractual cash flow characteristics of the financial asset.
In addition, IFRS 9 will require the impairment of financial assets to be calculated using an expected credit loss model that replaces the incurred loss impairment model required by IAS 39. For financial liabilities, there were no changes to classification and measurement, except for the recognition of changes in own credit risk in other comprehensive income for financial liabilities designated at fair value through profit or loss. The Group has not yet assessed the full impact of adopting IFRS 9, which is effective for financial periods beginning on or after 1 January 2022 as described above.
IFRS 16 Leases (IFRS 16) sets out the principles for the recognition, measurement, presentation and disclosure of leases. All leases result in the lessee obtaining the right to use an asset at the start of the lease and, if lease payments are made over time, also obtaining financing. Accordingly, IFRS 16 eliminates the classification of leases as either operating leases or finance leases as is required by IAS 17 Leases (IAS 17) and, instead, introduces a single lessee accounting model.