Page 36 - Ecuador's Banana Sector under Climate Change
P. 36
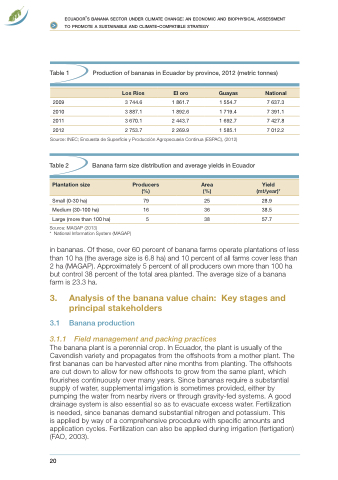
Table 1
2009
2010
2011
2012
Production of bananas in Ecuador by province, 2012 (metric tonnes)
ecuador’s banana sector under climate change: an economic and biophysical assessment to promote a sustainable and climate-compatible strategy
Table 2
Plantation size
Small (0-30 ha)
Medium (30-100 ha) Large (more than 100 ha)
Source: MAGAP (2013)
* National Information System (MAGAP)
3.
3.1
3.1.1
Analysis of the banana value chain: Key stages and principal stakeholders
Banana production
Field management and packing practices
Los Rios
3 744.6 3 887.1 3 670.1 2 753.7
El oro
1 861.7
1 892.6 2 443.7 2 269.9
Guayas
1 554.7 1 719.4 1 692.7 1 585.1
National
7 637.3 7 391.1 7 427.8 7 012.2
Yield
(mt/year)*
28.9 38.5 57.7
Source: INEC; Encuesta de Superficie y Producción Agropecuaria Continua (ESPAC), (2012)
Banana farm size distribution and average yields in Ecuador
Producers Area
(%) (%)
79 25 16 36 5 38
in bananas. Of these, over 60 percent of banana farms operate plantations of less than 10 ha (the average size is 6.8 ha) and 10 percent of all farms cover less than 2 ha (MAGAP). Approximately 5 percent of all producers own more than 100 ha but control 38 percent of the total area planted. The average size of a banana farm is 23.3 ha.
The banana plant is a perennial crop. In Ecuador, the plant is usually of the Cavendish variety and propagates from the offshoots from a mother plant. The first bananas can be harvested after nine months from planting. The offshoots are cut down to allow for new offshoots to grow from the same plant, which flourishes continuously over many years. Since bananas require a substantial supply of water, supplemental irrigation is sometimes provided, either by pumping the water from nearby rivers or through gravity-fed systems. A good drainage system is also essential so as to evacuate excess water. Fertilization is needed, since bananas demand substantial nitrogen and potassium. This
is applied by way of a comprehensive procedure with specific amounts and application cycles. Fertilization can also be applied during irrigation (fertigation) (FAO, 2003).
20