Page 350 - Libro 2
P. 350
330 PART 5 — ABDOMINAL
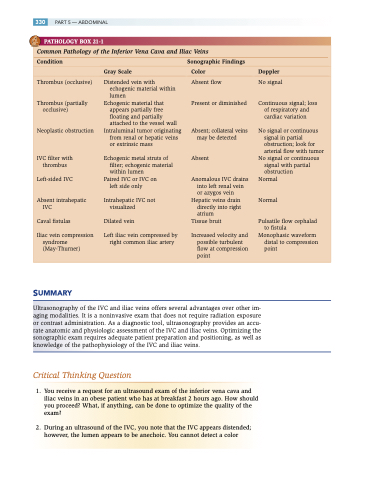
PATHOLOGY BOX 21-1
Common Pathology of the Inferior Vena Cava and Iliac Veins
Condition Sonographic Findings
Gray Scale Color Doppler
Thrombus (occlusive)
Thrombus (partially occlusive)
Neoplastic obstruction
IVC filter with thrombus
Left-sided IVC
Absent intrahepatic IVC
Caval fistulas
Iliac vein compression syndrome (May-Thurner)
Distended vein with echogenic material within lumen
Echogenic material that appears partially free floating and partially attached to the vessel wall
Intraluminal tumor originating from renal or hepatic veins or extrinsic mass
Echogenic metal struts of filter; echogenic material within lumen
Paired IVC or IVC on left side only
Intrahepatic IVC not visualized
Dilated vein
Left iliac vein compressed by right common iliac artery
Absent flow
Present or diminished
Absent; collateral veins may be detected
Absent
Anomalous IVC drains into left renal vein or azygos vein
Hepatic veins drain directly into right atrium
Tissue bruit
Increased velocity and possible turbulent flow at compression point
No signal
Continuous signal; loss of respiratory and cardiac variation
No signal or continuous signal in partial obstruction; look for arterial flow with tumor
No signal or continuous signal with partial obstruction
Normal
Normal
Pulsatile flow cephalad to fistula
Monophasic waveform distal to compression point
SUMMARY
Ultrasonography of the IVC and iliac veins offers several advantages over other im- aging modalities. It is a noninvasive exam that does not require radiation exposure or contrast administration. As a diagnostic tool, ultrasonography provides an accu- rate anatomic and physiologic assessment of the IVC and iliac veins. Optimizing the sonographic exam requires adequate patient preparation and positioning, as well as knowledge of the pathophysiology of the IVC and iliac veins.
Critical Thinking Question
1. You receive a request for an ultrasound exam of the inferior vena cava and iliac veins in an obese patient who has at breakfast 2 hours ago. How should you proceed? What, if anything, can be done to optimize the quality of the exam?
2. During an ultrasound of the IVC, you note that the IVC appears distended; however, the lumen appears to be anechoic. You cannot detect a color