Page 16 - Covid19_Apr_30
P. 16
inorganic hybrid nanocoating based on silica nanoparticles coupled with a polymer matrix that is hydrophobic and disinfects the pathogenic virus associated with COVID-19 that comes in contact with the surface of the mask.
Website link:
https://dst.gov.in/organic-inorganic-hybrid-nanocoatings-disposable-masks-formidable-arsenal-against-pathogen- ic-covid
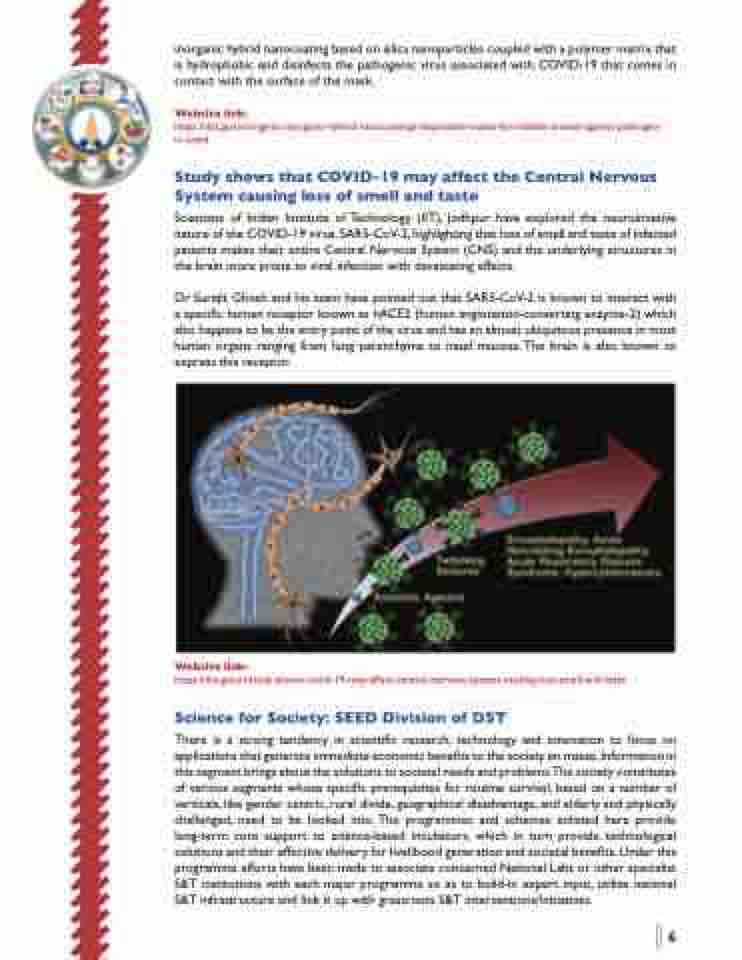
Study shows that COVID-19 may affect the Central Nervous
System causing loss of smell and taste
Scientists of Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Jodhpur have explored the neuroinvasive nature of the COVID-19 virus, SARS-CoV-2, highlighting that loss of smell and taste of infected patients makes their entire Central Nervous System (CNS) and the underlying structures in the brain more prone to viral infection with devastating effects.
Dr Surajit Ghosh and his team have pointed out that SARS-CoV-2 is known to interact with a specific human receptor known as hACE2 (human angiotensin-converting enzyme-2) which also happens to be the entry point of the virus and has an almost ubiquitous presence in most human organs ranging from lung parenchyma to nasal mucosa. The brain is also known to express this receptor.
Website link:
https://dst.gov.in/study-shows-covid-19-may-affect-central-nervous-system-causing-loss-smell-and-taste
Science for Society: SEED Division of DST
There is a strong tendency in scientific research, technology and innovation to focus on applications that generate immediate economic benefits to the society en masse. Information in this segment brings about the solutions to societal needs and problems.The society constitutes of various segments whose specific prerequisites for routine survival, based on a number of verticals, like gender centric, rural divide, geographical disadvantage, and elderly and physically challenged, need to be looked into. The programmes and schemes enlisted here provide long-term core support to science-based incubators, which in turn provide technological solutions and their effective delivery for livelihood generation and societal benefits. Under this programme efforts have been made to associate concerned National Labs or other specialist S&T institutions with each major programme so as to build-in expert input, utilize national S&T infrastructure and link it up with grassroots S&T interventions/initiatives.
6