Page 205 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 205
MECHANISMS FOR MOTION TRANSMISSION 191
Torque
T imp at N = 0.0
w
T eng at full throttle T imp at N = 0.2
w
T imp at N = 0.4
w
Stall point
Engine speed
(a)
Rimpull force Rimpull power
Gear 3 Gear 4
Gear 1 Gear 2 Gear 5
Gear 1
Gear 2
Gear 3
Gear 4
Gear 5
Machine speed Machine speed
(b) (c)
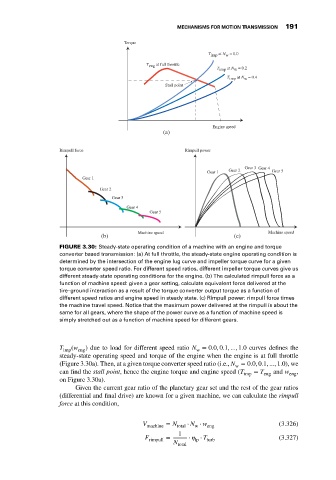
FIGURE 3.30: Steady-state operating condition of a machine with an engine and torque
converter based transmission: (a) At full throttle, the steady-state engine operating condition is
determined by the intersection of the engine lug curve and impeller torque curve for a given
torque converter speed ratio. For different speed ratios, different impeller torque curves give us
different steady-state operating conditions for the engine. (b) The calculated rimpull force as a
function of machine speed: given a gear setting, calculate equivalent force delivered at the
tire–ground interaction as a result of the torque converter output torque as a function of
different speed ratios and engine speed in steady state. (c) Rimpull power: rimpull force times
the machine travel speed. Notice that the maximum power delivered at the rimpull is about the
same for all gears, where the shape of the power curve as a function of machine speed is
simply stretched out as a function of machine speed for different gears.
T imp (w eng ) due to load for different speed ratio N = 0.0, 0.1, ...,1.0 curves defines the
w
steady-state operating speed and torque of the engine when the engine is at full throttle
(Figure 3.30a). Then, at a given torque converter speed ratio (i.e., N = 0.0, 0.1, ...,1.0), we
w
can find the stall point, hence the engine torque and engine speed (T imp = T eng and w eng ,
on Figure 3.30a).
Given the current gear ratio of the planetary gear set and the rest of the gear ratios
(differential and final drive) are known for a given machine, we can calculate the rimpull
force at this condition,
V machine = N total ⋅ N ⋅ w eng (3.326)
w
1
F = ⋅ ⋅ T (3.327)
rimpull lp turb
N
total