Page 221 - Icon Ridge Presents ATORN
P. 221
Thread tools \ Technical introduction – thread forming
Lubrication grooves on thread formers
Process:
In contrast to tapping, where sections are cut out of the material, thread forming is a non-cutting, pressure forming procedure.
Advantages:
No chip formation
Up to 30% higher surface quality than with thread cutting
Up to 40% higher processing speed than with thread cutting
Threads in through holes and blind holes can be produced with the same tool
Wide range of materials processable
Cutting of thread eliminated
Thread pitch and thread angle errors as with cut threads eliminated
Shaped threads have higher strength owing to non-continuous cut
Requirements: For all shapeable materials with elongation >10 %.
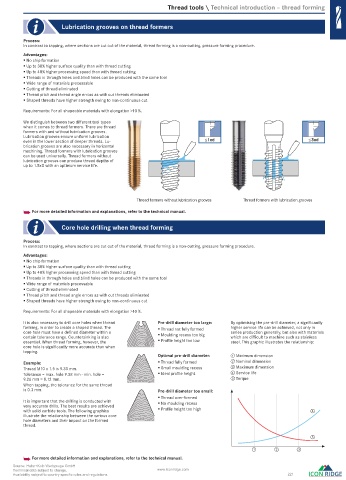
We distinguish between two diff erent tool types
when it comes to thread formers. There are thread
formers with and without lubrication grooves.
Lubrication grooves ensure uniform lubrication
even in the lower section of deeper threads. Lu- 1xd 3xd
brication grooves are also necessary in horizontal
machining. Thread formers with lubrication grooves
can be used universally. Thread formers without
lubrication grooves can produce thread depths of
up to 1.5xD with an optimum service life.
Thread formers without lubrication grooves Thread formers with lubrication grooves
h For more detailed information and explanations, refer to the technical manual.
Core hole drilling when thread forming
Process:
In contrast to tapping, where sections are cut out of the material, thread forming is a non-cutting, pressure forming procedure.
Advantages:
No chip formation
Up to 30% higher surface quality than with thread cutting
Up to 40% higher processing speed than with thread cutting
Threads in through holes and blind holes can be produced with the same tool
Wide range of materials processable
Cutting of thread eliminated
Thread pitch and thread angle errors as with cut threads eliminated
Shaped threads have higher strength owing to non-continuous cut
Requirements: For all shapeable materials with elongation >10 %.
It is also necessary to drill core holes when thread Pre-drill diameter too large: By optimising the pre-drill diameter, a signifi cantly
forming, in order to create a shaped thread. The Thread not fully formed higher service life can be achieved, not only in
core hole must have a defi ned diameter within a Moulding recess too big series production generally, but also with materials
certain tolerance range. Countersinking is also which are diffi cult to machine such as stainless
essential. When thread forming, however, the Profi le height too low steel. This graphic illustrates the relationship:
core hole is signifi cantly more accurate than when
tapping.
Optimal pre-drill diameter: ① Minimum dimension
Example: Thread fully formed ② Nominal dimension
Thread M10 x 1.5 is 9.30 mm. Small moulding recess ③ Maximum dimension
Tolerance = max. hole 9.38 mm - min. hole = Ideal profi le height ④ Service life
9.26 mm = 0.12 mm. ⑤ Torque
When tapping, the tolerance for the same thread
is 0.3 mm. Pre-drill diameter too small:
Thread over-formed
It is important that the drilling is conducted with No moulding recess
very accurate drills. The best results are achieved
with solid carbide tools. The following graphics Profi le height too high 4
illustrate the relationship between the various core
hole diameters and their impact on the formed
thread.
5
1 2 3
h For more detailed information and explanations, refer to the technical manual.
Source: Hahn+Kolb Werkzeuge GmbH
Technical data subject to change. www.iconridge.com
Availability subject to country specific rules and regulations. 221
0257_EN_2018_KERN[21847103]-l.indd 257 12/17/2018 3:32:07 PM