Page 9 - Grp3-Soil magazine (Final-Vid ver)
P. 9
E
T
B
R
A
ATTERBERG LIMIT (Clay/Silt)
T
ATTERBERG LIMIT
E
L
I
M
R
T
G
I
PAGE 22
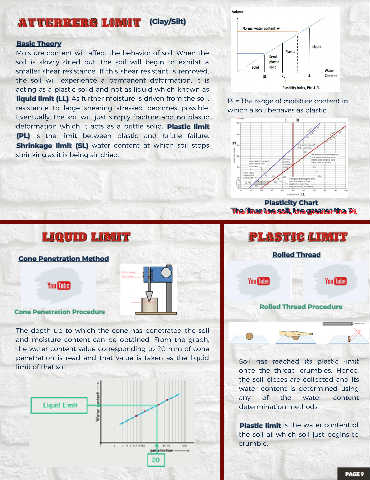
Basic Theory
Moisture content will affect the behavior of soil. When the
soil is slowly dried out, the soil will begin to exhibit a
smaller shear resistance. If this shear resistant is removed,
the soil will experience a permanent deformation, it is
acting as a plastic solid and not as liquid which known as
liquid limit (LL). As further moisture is driven from the soil,
PI = The range of moisture content in
resistance to large shearing stressed becomes possible.
which a soil behaves as plastic.
Eventually, the soil will just simply fracture and no plastic
solid. Plastic limit
deformation which it acts as a brittle
(PL) is the limit between plastic and brittle failure.
Shrinkage limit (SL) water content at which soil stops
shrinking as it is being air-dried.
Plasticity Chart
e
h
f
t
i
n
r
t
e
e
r
e
g
a
r
t
e
e
o
i
s
l
t
h
,
h
I
The finer the soil, the greater the PI.
The finer the soil, the greater the PI. .
T
P
e
h
I
I
Q
D
U
I
C
LIQUID LIMIT
LIQUID LIMIT PLASTIC LIMIT
L
M
I
L
T
PLASTIC LIMIT
L
A
I
T
P
T
I
S
M
I
L
Rolled Thread
Cone Penetration Method
Rolled Thread Procedure
Cone Penetration Procedure
The depth up to which the cone has penetrated the soil
and moisture content can be obtained. From the graph,
the water content value corresponding to 20 mm of cone
penetration is read and that value is taken as the liquid
Soil has reached its plastic limit
limit of that soil
once the thread crumbles. Hence,
the soil pieces are collected and its
water content is determined using
any of the water content
determination methods.
Plastic limit is the water content of
the soil at which soil just begins to
crumble.
PAGE 9