Page 140 - classs 6 a_Neat
P. 140
3.PQRS is a quadrilateral in which PQ = QR = RS = SP, PR = SQ. All angles, P, Q, R and S are equal and CUBOID
the diagonals bisect each other at right angles. Name the quadrilateral.
CUBOID Solids such as a wooden box, a matchbox, a brick, a book, an almirah, etc., are all in the shape of a
4.ABCD is a kite. Draw the figure and name the equal sides. Draw the diagonals AC and BD and let them meet at cuboid.
0. Is AOD = AOB? What is the measure of AOD and AOB? Some of these shapes are given below.
5. ABCD is a quadrilateral. AB = CD and AD = BC. All interior angles are equal to 90’. AC = BD. Name
the quadrilateral.
6. Distinguish between the following:
a. a square and a rectangle.
b. a square and a rhombus.
c. a trapezium and an isosceles trapezium.
A cuboid has length, breadth and height.
7. Write the names of the polygons with the following number of sides: Various parts of a cuboid are given below
a. six b. eight c. ten d. twelve e. four (i) FACES A cuboid has stx rectangular faces.
The opposite faces of a cuboid are identical.
8. A pentagon has sides measuring 5 cm, 6 cm, 7 cm, 5 cm and 10 cm. Is it a regular polygon? Give reasons.
9.In the parallelogram PQRS, _P is double of _Q. Find all the angles of the parallelogram. (ii) EDGES Too adjacent faces of a cuboid meet in a line segment,
called an edge of the cuboid. A cuboid has 12 edges.
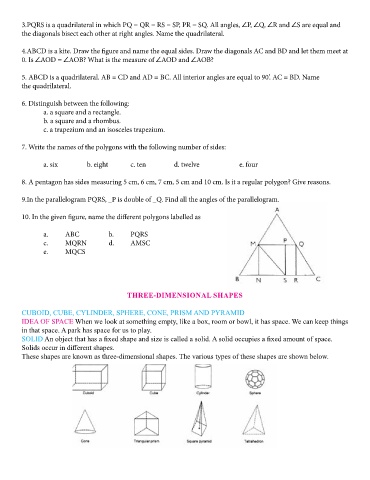
10. In the given figure, name the different polygons labelled as
(iii) VERTICES Three edges of a cuboid meet at a point, called a vertex.
a. ABC b. PQRS A cuboid has 8 vertices.
c. MQRN d. AMSC
e. MQCS Thus, a cuboid has 6 rectangular faces, 12 edges and 8 vertices.
CUBE
THREE-DIMENSIONAL SHAPES
CUBE A cuboid whose length, breadth and height are equal is called a cube.
CUBOID, CUBE, CYLINDER, SPHERE, CONE, PRISM AND PYRAMID
IDEA OF SPACE When we look at something empty, like a box, room or bowl, it has space. We can keep things
in that space. A park has space for us to play. EXAMPLES Ice cubes, sugar cubes, dice, etc., are all examples of a cube.
SOLID An object that has a fixed shape and size is called a solid. A solid occupies a fixed amount of space. Clearly, a cube has 6 square faces, 12 edges and 8 vertices.
Solids occur in different shapes.
These shapes are known as three-dimensional shapes. The various types of these shapes are shown below.
CYLINDER
CYLINDER Objects such as a circular pillar, a circular pipe, a test tube, a circular storage tank,
a measuring jar, a gas cylinder, a circular powder ttn, etc., are in the shape of a cylinder.
Some of these shapes are shown below.