Page 42 - M97TB9_2018-19_[low-res]_F2F_Neat2
P. 42
2/2 M97/February 2018 Reinsurance
Introduction
We have already considered the reasons why insurers contemplate the purchase of reinsurance, and the
2 benefits that are conferred upon the insurer (i.e. the reinsured, the cedant or the ceding company) once
Chapter reinsurance available to the insurer and the factors that are taken into account when selecting one type
the contract of reinsurance has been finalised. In this chapter, we will examine the different types of
in preference to another.
Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages and these will be considered as we focus on each
type of reinsurance in turn. Reinsurance can be divided into two main types:
• Facultative – the individual reinsurance of large or hazardous single risks which we look at in more
detail in chapter 3.
• Treaty – a contract that automatically accepts a large number of similar risks.
These types can be further divided into two basic methods:
• Proportional, which will be explained in detail in chapter 4.
• Non-proportional, which will be explained in detail in chapter 5.
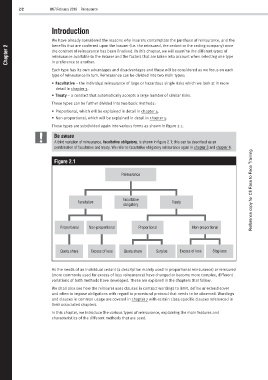
These types are subdivided again into various forms as shown in figure 2.1.
Be aware
A third variation of reinsurance, facultative obligatory, is shown in figure 2.1; this can be described as an
combination of facultative and treaty. We refer to facultative obligatory reinsurance again in chapter 3 and chapter 4.
Figure 2.1
Reinsurance
Facultative Reference copy for CII Face to Face Training
Facultative Treaty
obligatory
Proportional Non-proportional Proportional Non-proportional
Quota share Excess of loss Quota share Surplus Excess of loss Stop loss
As the needs of an individual cedant (a description mainly used in proportional reinsurance) or reinsured
(more commonly used for excess of loss reinsurance) have changed or become more complex, different
variations of both methods have developed. These are explored in the chapters that follow.
We shall also see how the reinsurer uses clauses in contract wordings to limit, define or extend cover
and often to impose obligations with regard to procedural protocol that needs to be observed. Wordings
and clauses in common usage are covered in chapter 7 with certain class-specific clauses referenced in
their associated chapters.
In this chapter, we introduce the various types of reinsurance, explaining the main features and
characteristics of the different methods that are used.