Page 28 - Introduction QC
P. 28
GMP Training – Introduction to Quality Control (QC) by www.gmpsop.com
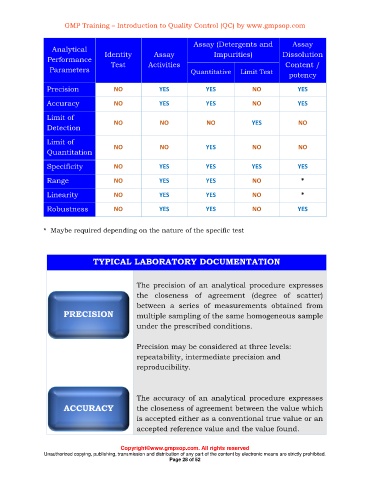
Assay (Detergents and Assay
Analytical
Assay
Performance Identity Activities Impurities) Dissolution
Test
Content /
Parameters Quantitative Limit Test potency
Precision NO YES YES NO YES
Accuracy NO YES YES NO YES
Limit of
NO NO NO YES NO
Detection
Limit of
NO NO YES NO NO
Quantitation
Specificity NO YES YES YES YES
Range NO YES YES NO *
Linearity NO YES YES NO *
Robustness NO YES YES NO YES
* Maybe required depending on the nature of the specific test
TYPICAL LABORATORY DOCUMENTATION
The precision of an analytical procedure expresses
the closeness of agreement (degree of scatter)
between a series of measurements obtained from
PRECISION multiple sampling of the same homogeneous sample
under the prescribed conditions.
Precision may be considered at three levels:
repeatability, intermediate precision and
reproducibility.
The accuracy of an analytical procedure expresses
ACCURACY the closeness of agreement between the value which
is accepted either as a conventional true value or an
accepted reference value and the value found.
Copyright©www.gmpsop.com. All rights reserved
Unauthorized copying, publishing, transmission and distribution of any part of the content by electronic means are strictly prohibited.
Page 28 of 52