Page 7 - Industrial_Technology_EXTRA_14th Septembert_2020_Classical
P. 7
perception sensing modality and the need for object rather than safely avoiding it. LIDAR’s strong
multiple sensors in a system. object detection and classification accuracy
provides the precision necessary to complete these
Giving machines sight common tasks.
The challenges of Industry 4.0 are diverse. Limited Operating in the terahertz frequency range,
space and autonomously acting machinery (robots, LIDAR systems achieve fine angular resolution that
cobots, etc.) paired in hostile environments require translates into high resolution depth maps. With
radar technology that’s smaller in size, more these high-res depth maps, a LIDAR system can
accurate, and capable of measuring nearby targets. classify objects to fuse with vision, IMU, and radar
Imaging and classification of surrounding areas is information to make reliable, mission-critical
essential to efficiency, productivity, and safety. decisions. LIDAR systems are designed to work in
Driven by the latest advances in RF transceiver dynamic environments, such as outdoors in bright
IC technology, radar is quickly becoming one of the sunlight. By using narrow pulses of 9xx nm and
important sensor technologies for perception 15xx nm wavelengths, and driving them with high
applications. One example is 77 GHz fully integrated power, LIDAR is able to see farther in these
all-digital transceiver MMICs. High speed and challenging conditions. In addition, the narrow
linearity FMCW chirps combined with high output pulses allow for finer depth resolution to detect
power, low noise transmit and receive channels, and multiple targets within a pixel, while the infrared
MIMO antenna arrays now enable high performance, light at 9xx and 15xx has less solar radiation.
high resolution radar systems at reasonable cost. Numerous challenges must be overcome to
Radar-based digital beamforming enables detection encourage the mass adoption of LIDAR systems.
of radial velocity, angle, and distance to multiple These include complex and costly signal chains,
targets under the harshest environmental conditions optical design issues, and system test and
– it’s key for the safe and efficient interaction of calibration. Developments are currently underway
robots, cobots, and AGVs in dynamic environments. to integrate these signal chains and reduce their
The mission of an autonomous system in an complexity, size, power requirements, and overall
industrial setting is often to locate and pick up an cost of ownership.
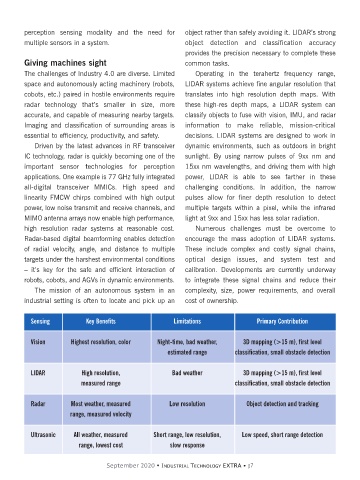
Sensing Key Benefits Limitations Primary Contribution
Vision Highest resolution, color Night-time, bad weather, 3D mapping (>15 m), first level
estimated range classification, small obstacle detection
LIDAR High resolution, Bad weather 3D mapping (>15 m), first level
measured range classification, small obstacle detection
Radar Most weather, measured Low resolution Object detection and tracking
range, measured velocity
Ultrasonic All weather, measured Short range, low resolution, Low speed, short range detection
range, lowest cost slow response
September 2020 • INDUSTRIAL TECHNOLOGY EXTRA • p7