Page 2 - BULLETIN HSB 2021
P. 2
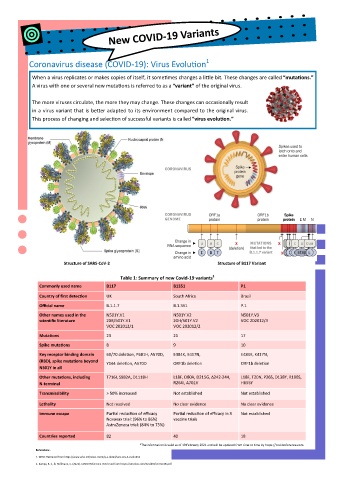
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Virus Evolution 1
When a virus replicates or makes copies of itself, it sometimes changes a little bit. These changes are called “mutations.”
A virus with one or several new mutations is referred to as a “variant” of the original virus.
The more viruses circulate, the more they may change. These changes can occasionally result
in a virus variant that is better adapted to its environment compared to the original virus.
This process of changing and selection of successful variants is called “virus evolution.”
Structure of SARS-CoV-2 Structure of B117 Variant
Table 1: Summary of new Covid-19 variants 2
Commonly used name B117 B1351 P1
Country of first detection UK South Africa Brazil
Official name B.1.1.7 B.1.351 P.1
Other names used in the N501Y.V1 N501Y.V2 N501Y.V3
scientific literature 20B/501Y.V1 20H/501Y.V2 VOC 202012/3
VOC 202012/1 VOC 202012/2
Mutations 23 21 17
Spike mutations 8 9 10
Key receptor binding domain 69/70 deletion, P681H, A570D, E484K, K417N, E484K, K417N,
(RBD), spike mutations beyond
Y144 deletion, A570D ORF1b deletion ORF1b deletion
N501Y in all
Other mutations, including T716I, S982A, D1118H L18F, D80A, D215G, ∆242-244, L18F, T20N, P26S, D138Y, R190S,
N-terminal R264I, A701V H655Y
Transmissibility > 50% increased Not established Not established
Lethality Not resolved No clear evidence No clear evidence
Immune escape Partial reduction of efficacy Partial reduction of efficacy in 3 Not established
Novavax trial: (96% to 86%) vaccine trials
AstraZeneca trial: (84% to 75%)
Countries reported 82 40 18
*The information is valid as of 19 February 2021 and will be updated from time to time by https://covidreference.com
References:-
1. WHO: Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/sars-cov-2-evolution
2. Kamps, B. S., & Hoffmann, C. (2021). COVID Reference. Retrieved from https://amedeo.com/CovidReference06.pdf