Page 489 - The History of the Royal Army Veterinary Corps 1962–2021
P. 489
THE HISTORY OF THE ROYAL ARMY VETERINARY CORPS 1962 – 2021
2007: “Heat Illness.28 There have been no cases of heat related illness concerning MWDs in theatre to date. Heat stress management welfare checks are conducted every hour during daylight hours. The Unit regrets not taking the internal temperature of the ISO kennel systems for record purposes. This aspect has commenced wef 10th June 2007. The ISOs appear cooler than the tentage office, which is thought to be due to the flow of air through ISOs – one main door and six kennel doors, as opposed to the two doors of the office tent and the fact the ISOs are well insulated. Both the ISOs and tentage office are shielded from direct sunlight with cam nets which reduces the temperature significantly.”
The very hot temperatures encountered, particularly on the makeshift front gate at BSN, meant handlers were working in direct sunlight, in 30 – 49°C heat, with no shade during all parts of the day. Working in helmets and Osprey body armour, carrying rifles, and a generous supply of additional water to hydrate dogs, due to consider- ation was given to mitigating the risk of heat illness for both dogs and handlers. However, in the heat and dust, carrying cumbersome equipment while
28 TMWDSU Operational Update/102/G7/2 dated 18th June 2007. 29 TMWDSU/102/J1/01 dated 28th April 2007.
30 TMWDSU Operational Update/102/G7/2 dated 18th June 2007.
needing to enter vehicles with high cabs, the duties were tiring. Added to that, the continual need to search human waste slurry tankers entering the camp prompted a case to be put forward for AES, VS and Protection dog handlers to receive an Unpleasant Working Allowance; this was duly staffed, and handlers received the daily allowance for their entire tour.29
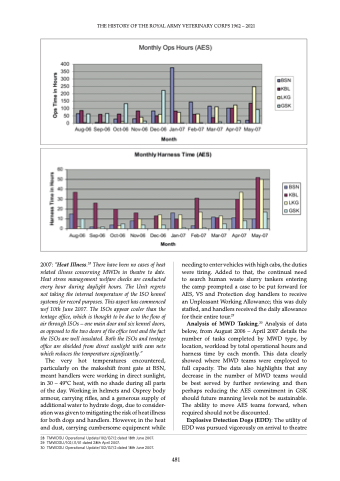
Analysis of MWD Tasking.30 Analysis of data below, from August 2006 – April 2007 details the number of tasks completed by MWD type, by location, workload by total operational hours and harness time by each month. This data clearly showed where MWD teams were employed to full capacity. The data also highlights that any decrease in the number of MWD teams would be best served by further reviewing and then perhaps reducing the AES commitment in GSK should future manning levels not be sustainable. The ability to move AES teams forward, when required should not be discounted.
Explosive Detection Dogs (EDD): The utility of EDD was pursued vigorously on arrival to theatre
481