Page 18 - Threat Intelligence 8-21-2019
P. 18
Infographic of
the Week
The main goal of DMARC is to detect and prevent email spoofing. For example, phishing scams using
domains from banks to send out email on their behalf. Customers from that bank think they receive a legit
email, that their bank card isn’t valid anymore. The link to click on will lead to a fraudulent website. This
website is exactly the same as the real website and logging in will provide the cyber criminals the possibility
to use your credentials.
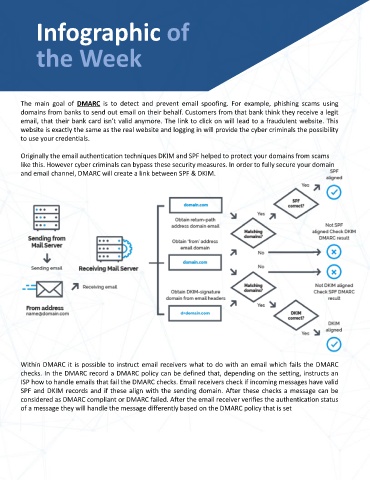
Originally the email authentication techniques DKIM and SPF helped to protect your domains from scams
like this. However cyber criminals can bypass these security measures. In order to fully secure your domain
and email channel, DMARC will create a link between SPF & DKIM.
Within DMARC it is possible to instruct email receivers what to do with an email which fails the DMARC
checks. In the DMARC record a DMARC policy can be defined that, depending on the setting, instructs an
ISP how to handle emails that fail the DMARC checks. Email receivers check if incoming messages have valid
SPF and DKIM records and if these align with the sending domain. After these checks a message can be
considered as DMARC compliant or DMARC failed. After the email receiver verifies the authentication status
of a message they will handle the message differently based on the DMARC policy that is set