Page 7 - Structural Highway Design_Neat
P. 7
4.2. Rigid Pavement
A rigid pavement structure is composed of a hydraulic cement concrete surface
course, and underlying base and subbase courses (if used). Rigid pavements can
have reinforcing steel, which is generally used to handle thermal stresses to reduce
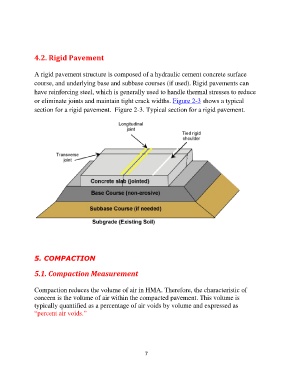
or eliminate joints and maintain tight crack widths. Figure 2-3 shows a typical
section for a rigid pavement. Figure 2-3. Typical section for a rigid pavement.
5. COMPACTION
5.1. Compaction Measurement
Compaction reduces the volume of air in HMA. Therefore, the characteristic of
concern is the volume of air within the compacted pavement. This volume is
typically quantified as a percentage of air voids by volume and expressed as
“percent air voids.”
7