Page 21 - Clinical Biochemistry
P. 21
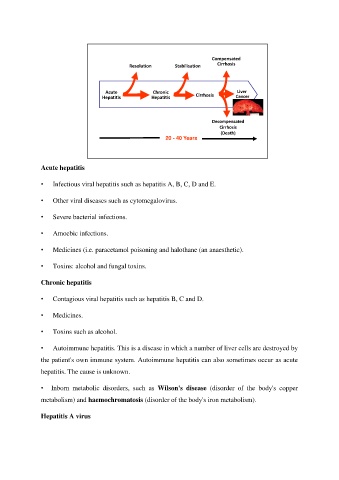
Resolution Stabilisation Compensated
Cirrhosis
Acute Chronic Cirrhosis Liver
Hepatitis Hepatitis Cancer
Decompensated
Cirrhosis
(Death)
20 - 40 Years
Acute hepatitis
• Infectious viral hepatitis such as hepatitis A, B, C, D and E.
• Other viral diseases such as cytomegalovirus.
• Severe bacterial infections.
• Amoebic infections.
• Medicines (i.e. paracetamol poisoning and halothane (an anaesthetic).
• Toxins: alcohol and fungal toxins.
Chronic hepatitis
• Contagious viral hepatitis such as hepatitis B, C and D.
• Medicines.
• Toxins such as alcohol.
• Autoimmune hepatitis. This is a disease in which a number of liver cells are destroyed by
the patient's own immune system. Autoimmune hepatitis can also sometimes occur as acute
hepatitis. The cause is unknown.
• Inborn metabolic disorders, such as Wilson's disease (disorder of the body's copper
metabolism) and haemochromatosis (disorder of the body's iron metabolism).
Hepatitis A virus