Page 20 - Cell biology PDG 2024
P. 20
1) Active transport
Active transport is the movement of materials against a concentration
gradient (low concentration ⇒ high concentration) across the cell
membrane.
Because materials are moving against the gradient, it requires the
expenditure of energy (e.g. ATP hydrolysis)
Example of active transport: endocytosis, exocytosis and sodium
potassium pump
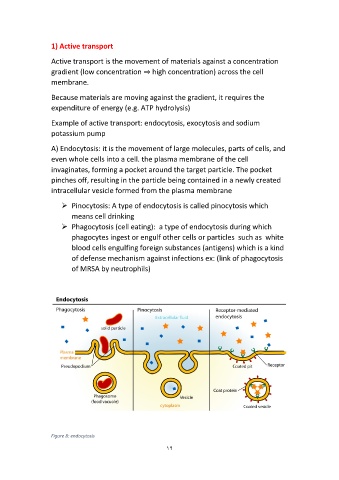
A) Endocytosis: it is the movement of large molecules, parts of cells, and
even whole cells into a cell. the plasma membrane of the cell
invaginates, forming a pocket around the target particle. The pocket
pinches off, resulting in the particle being contained in a newly created
intracellular vesicle formed from the plasma membrane
Pinocytosis: A type of endocytosis is called pinocytosis which
means cell drinking
Phagocytosis (cell eating): a type of endocytosis during which
phagocytes ingest or engulf other cells or particles such as white
blood cells engulfing foreign substances (antigens) which is a kind
of defense mechanism against infections ex: (link of phagocytosis
of MRSA by neutrophils)
Figure 8: endocytosis
۱۹