Page 122 - Medecinal plants clinical
P. 122
2. Condensed Tannins (Proanthocyanidins):
- These include all other true tannins, their molecules are more resistant to
breakage than hydrolysable tannins.
- On treatment with acids or enzymes they are decomposed into red
insoluble compounds known as “phlobaphenes”. Phlobaphenes give the
characteristic red colour to many drugs such as red cinchona bark.
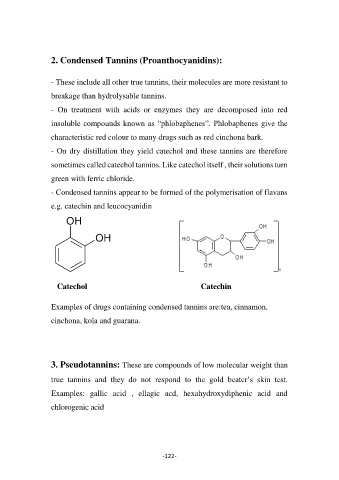
- On dry distillation they yield catechol and these tannins are therefore
sometimes called catechol tannins. Like catechol itself , their solutions turn
green with ferric chloride.
- Condensed tannins appear to be formed of the polymerisation of flavans
e.g. catechin and leucocyanidin
OH
OH
Catechol Catechin
Examples of drugs containing condensed tannins are:tea, cinnamon,
cinchona, kola and guarana.
3. Pseudotannins: These are compounds of low molecular weight than
true tannins and they do not respond to the gold beater’s skin test.
Examples: gallic acid , ellagic acd, hexahydroxydiphenic acid and
chlorogenic acid
-122-